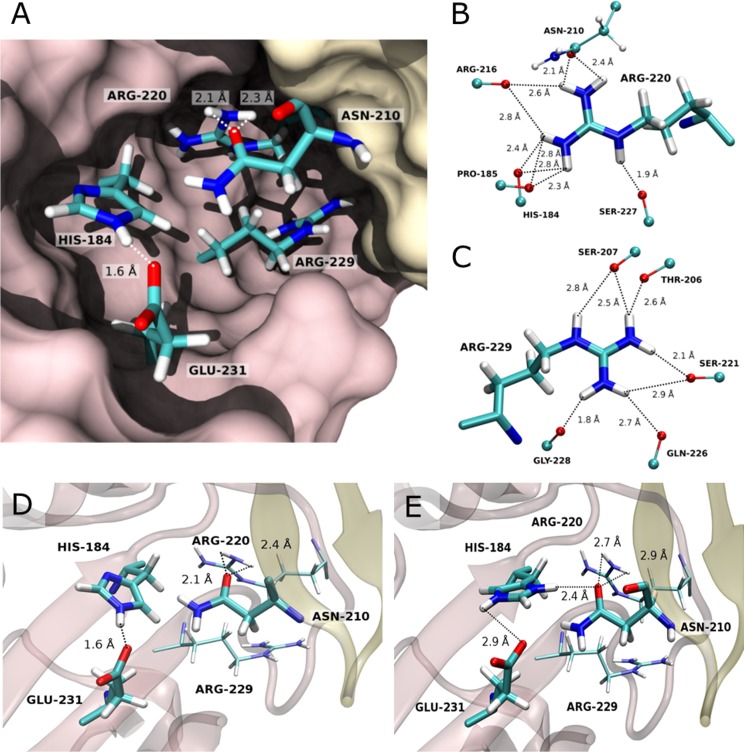
FIG 5.
Interactions of His184 and of neighboring residues at the HA1-HA1 interface in its neutral (A and D) and doubly protonated (E) states (PDB ID 2IBX). (A) Interactions at the HA1-HA1 interface. Monomers (chain A in brown and chain E in yellow) are depicted in surface representation, and residues which might be crucial for the regulation of HA1 monomer dissociation are shown in stick model. (B and C) Hydrogen bond network of residues Arg220 and Arg229. Interactions are formed between the polar atoms of residues Arg220 (B) and Arg229 (C) with those of the backbone amides, except for Asn210, where the hydrogen bond is formed with the side chain carbonyl-oxygen. The hydrogens were modeled as described in Materials and Methods. (D and E) Crystal structure of the HA1-HA1 interface at neutral pH (PDB ID 2IBX) (D) and its modeled conformation upon protonation of His184 at a pH below 5 (E). Secondary structures of chains A (brown) and E (yellow) are displayed in cartoon representation with residues His184, Arg216, Glu231, and Asn210 in stick model. For the modeling, the side chain of His184 has been rotated by 180 degrees, and the structure has been subsequently energy minimized. We suggest that a strong hydrogen bond is formed between His184 and Asn210, while the interaction between Asn210 and Arg220 is significantly weakened.