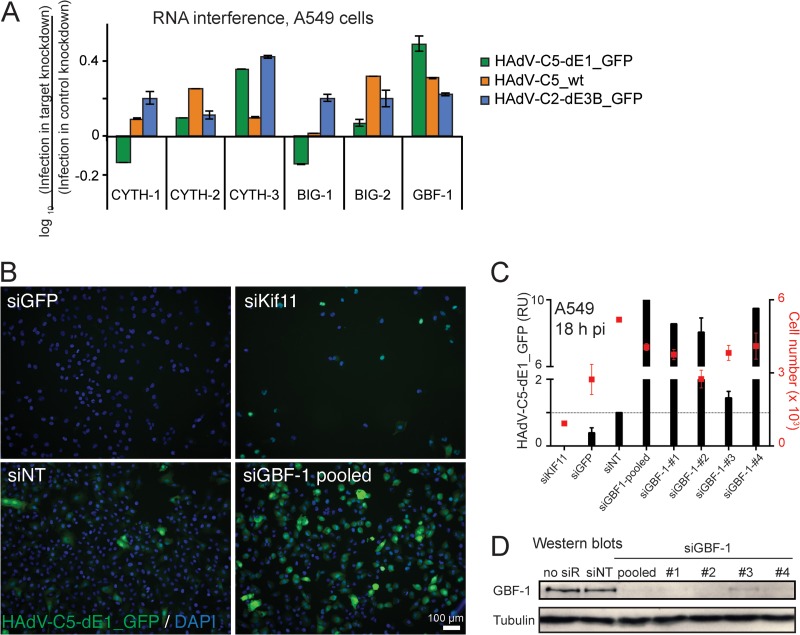
FIG 1.
Knockdown of GBF-1 enhances HAdV infections. (A) RNA interference miniscreen against Arf GEFs identifies GBF-1 knockdown as an enhancer of HAdV-C5-dE1_GFP, HAdV-C5_wt, and HAdV-C2-dE3B_GFP infections. Cells were reverse transfected with pooled siRNAs (1 pmol/well) against cytohesin 1 (CYTH-1), CYTH-2, CYTH-3, brefeldin A-inhibited guanine nucleotide exchange protein 1 (BIG-1), BIG-2, or GBF-1 for 48 h, infected as indicated, fixed at 18 h p.i., and analyzed for infection. Results are expressed as the log10 ratio of the mean nuclear intensity of GFP in infected cells normalized to that in control cells transfected with nontargeting siRNA. (B to D) Knockdown of GBF-1 siRNA (siGBF-1) enhances HAdV-C5-dE1_GFP infection in A549 cells. Single or pooled GBF-1 siRNAs, along with control nontargeting siRNA (siNT), kinesin family member protein 11 siRNA (siKif11), and GFP siRNA (siGFP), were reverse transfected into A549 cells, and cells were infected at 48 h posttransfection. At 18 h postinfection, the cells were fixed, stained with DAPI, and analyzed for infection. (B) Representative images. (C) Quantification of the GFP signal in cells transfected with the indicated siRNAs. RU, relative units, representing the mean nuclear GFP signal from three parallel samples ± SDs. The cell toxicity of the siRNAs was measured by use of the cell number shown on the secondary x axis. (D) Western blots. no siR, no siRNA.