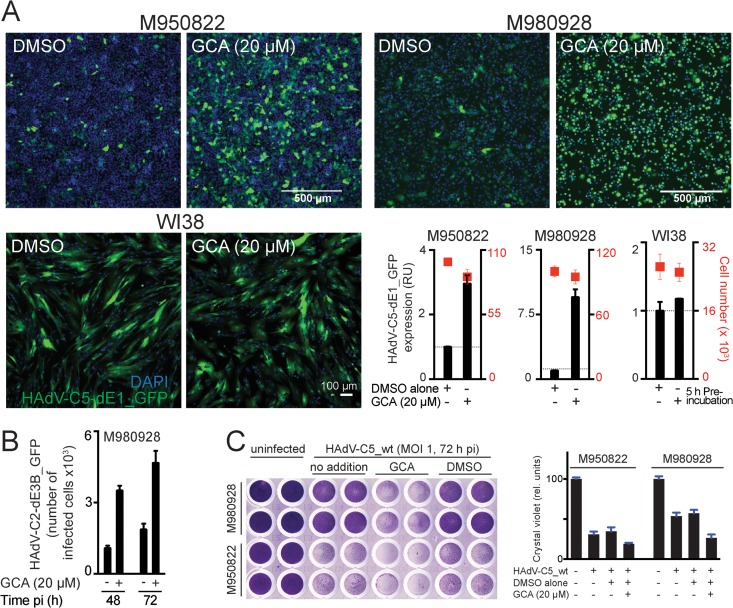
FIG 4.
GBF-1 inhibition enhances adenovirus infection of melanoma cells. (A) Inhibition of GBF-1 by GCA enhances HAdV-C5-dE1_GFP infection of M950822 and M980928 melanoma cells but not normal human WI38 fibroblasts. Cells were preincubated with DMSO or GCA for 5 h, inoculated with the virus, and analyzed at 18 h p.i. Shown are representative images and quantification of the mean nuclear GFP signal. (B) Inhibition of GBF-1 enhances HAdV-C2-dE3B_GFP spreading in melanoma-derived M980928 cells. The cells were preincubated with DMSO or GCA for 5 h and inoculated with the virus (MOI, ∼0.00016). The data are from a live experiment in which recordings were made every 4 h to 5 h. Shown is the number of GFP-positive cells at 48 h and 72 h p.i. (C) Inhibition of GBF-1 enhances HAdV-C5_wt-induced killing of M950822 and M980928 cells. The cells were preincubated with DMSO or GCA for 5 h, inoculated with HAdV-C5_wt (MOI, 1), and stained with crystal violet at 72 h p.i. (left). (Right) Quantification of crystal violet staining, which is proportional to cell numbers. rel. units, relative units.