FIG 2.
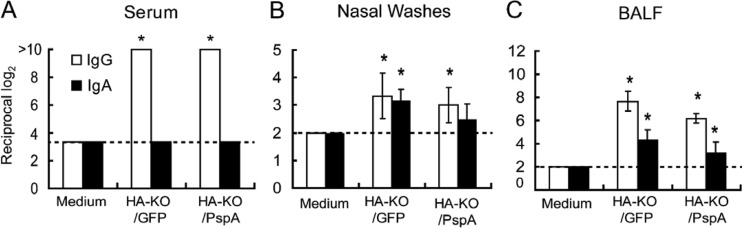
Induction of influenza virus-specific IgG and IgA in serum (A), nasal wash (B), and BALF (C) samples. Mice were intranasally inoculated with medium, HA-KO/GFP virus, or HA-KO/PspA virus with a 2-week interval between the inoculations. Samples from six mice from each group were collected 2 weeks after the final vaccination. Virus-specific antibodies were detected by using an ELISA. Results are expressed as the means of the reciprocal titer log2 (± standard deviations [SD]). Statistically significant differences between groups were determined by using the Dunnett method. The asterisk indicates a significant difference from samples taken from mice inoculated with medium (*, P < 0.05). The broken lines indicate the detection limits.
