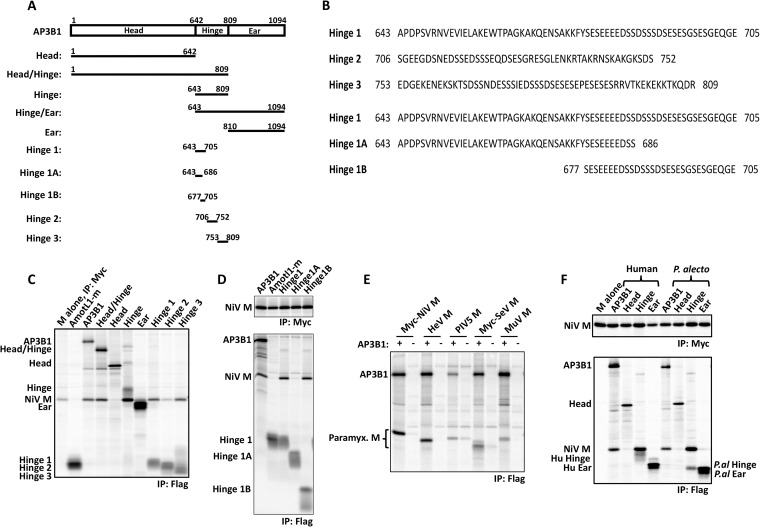
FIG 3.
Small AP3B1-derived polypeptides bind Nipah virus M protein. (A) Schematic representation of human AP3B1 and AP3B1-derived polypeptides. (B) Amino acid sequences of human AP3B1 Hinge-derived polypeptides. (C to F) 293T cells were transfected to produce Myc-tagged Nipah virus M protein (C, D, and F) or the indicated paramyxovirus M proteins (E) together with the indicated Flag-tagged AP3B1-derived polypeptides, and coimmunoprecipitation was carried out as described in the legend to Fig. 2. The bat (P. alecto)-derived AP3B1-derived polypeptides used for panel F are the equivalents of the corresponding human segments illustrated in panel A, based on ClustalW2 sequence alignment between the human and P. alecto AP3B1 proteins. The upper gels in panels D and F correspond to control immunoprecipitations of Myc-M protein using Myc antibody, while the lower gels correspond to coimmunoprecipitation experiments using Flag antibody.