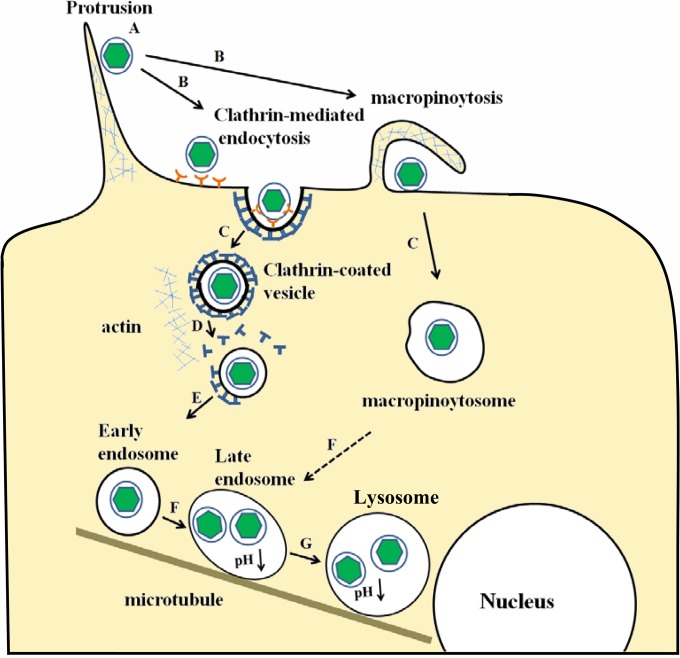
FIG 10.
Model entry route of SGIV into GS cells. A, SGIV particles may transport along actin-rich protrusions to reach the cell surface. B, internalization of SGIV particles by clathrin-mediated endocytosis and macropinocytosis. C, internalized particles contained within CCVs and macropinosomes. D, CCVs containing individual SGIV particles are rapidly uncoated. E, the virus is transported to the EE. F, an EE matures into an LE by decreasing its pH, and the macropinosome may also undergo acidification. G, further acidification brings the LE to the LY. C and D may represent actin-dependent movement, while E, F, and G may represent microtubule-dependent movement.