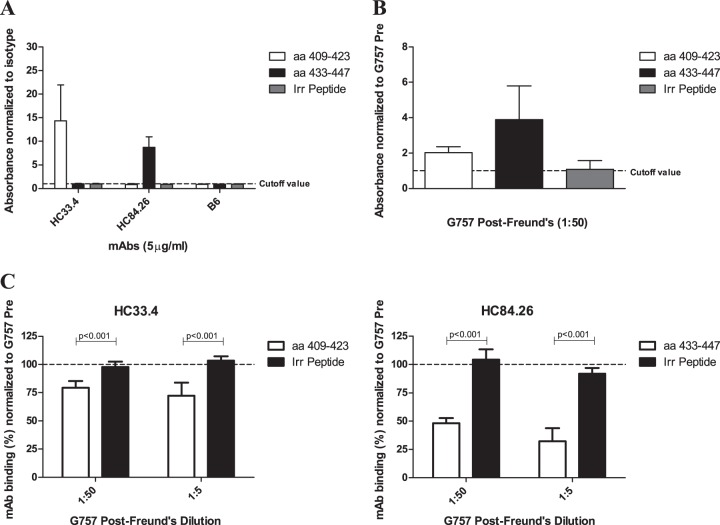
FIG 4.
Binding of immunized-goat antisera and MAbs to linear-synthetic biotinylated peptides by ELISA. (A and B) Human MAbs (HC33.4, HC84.26, and human IgG1 isotype control B6) at 5 μg/ml (A) or immunized-goat antisera from G757 diluted 1:50 (B) were incubated with biotinylated peptides precaptured in NeutrAvidin-coated microtiter plate wells. Two peptides from E2 (aa 409 to 423 and aa 433 to 447) and an irrelevant (Irr) biotinylated peptide of similar length were used (see Materials and Methods for the sequences). Binding was detected with species-specific AP-conjugated secondary antibodies. The results are presented as fold binding signal to peptide over the cutoff value. The cutoff value was determined by the mean binding to the same peptide plus 3 standard deviations by either G757 Pre (A) or human IgG1 isotype control MAb B6 (B). (C) The ability of goat sera to compete with MAb binding to peptide was determined. Diluted goat antisera were added to wells containing peptide for 1 hour, followed by incubation of the MAb at 5 μg/ml. The MAb and the target peptide are indicated. Binding of the MAbs was detected, and the percent MAb binding in the presence of G757 antisera was normalized to binding in the presence of G757 Pre. The error bars show standard deviations of all replicates from at least two independent experiments done in triplicate. Statistical evaluation comparing the competition with the binding of MAbs to target peptide or irrelevant peptide was performed using a two-tailed unpaired t test, and the P values are shown.