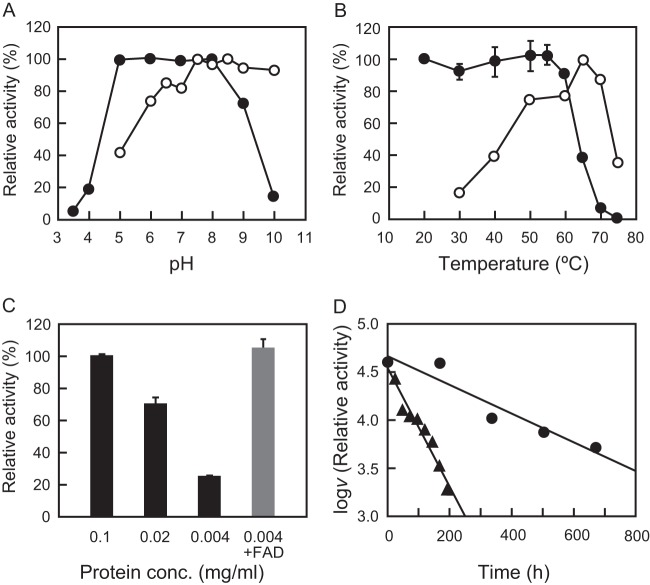
FIG 4.
Effect of pH, temperature, protein concentration, and FAD on the enzyme activity and stability of RxDAO. (A) Effect of pH on the enzyme activity (○) was determined by measuring the activity at the indicated pH values at 55°C. Effect of pH on the enzyme stability (●) was determined by measuring the remaining activity at pH 8.0 after incubation of the enzyme (0.1 mg/ml) at various pH values at 50°C for 1 h. (B) Effect of temperature on the enzyme activity (○) was determined by measuring the activity at the indicated temperatures at pH 8.0. Effect of temperature on the enzyme stability (●) was determined by measuring the remaining activity after incubation of the enzyme (0.1 mg/ml) at the indicated temperatures for 1 h. (C) Effect of enzyme protein concentration on the enzyme stability was determined by measuring the remaining activity after incubation at 60°C for 1 h. The gray bar represents the effect of 100 μM FAD on thermal denaturation. (D) The long-term thermal stability of the enzyme was determined by measuring the activity during the incubation of the enzyme (0.1 mg/ml) at 30°C (●) and 50°C (▲) at pH 8.0. The assays for pH, thermal, and long-term thermal stabilities and the effect of the enzyme concentration were performed using a coupled o-dianisidine/peroxidase method at 60°C, and optimum pH was determined using a DNPH method at 55°C. The assay for optimum temperature was performed using an oxygen electrode. Each data point represents the mean ± the standard deviation of three measurements.