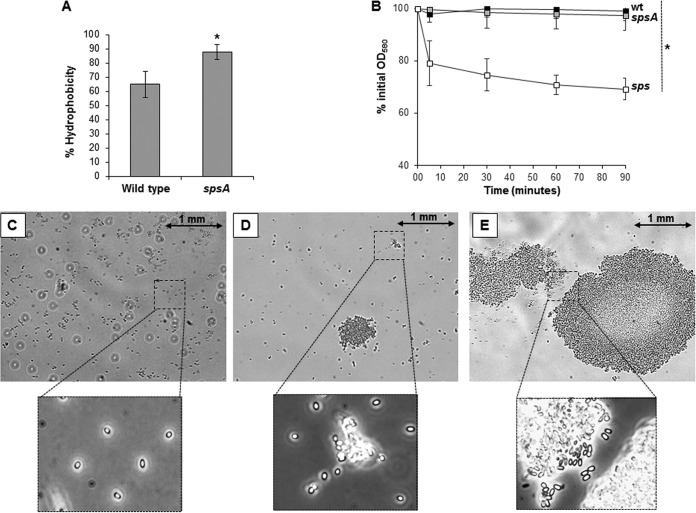
FIG 8.
(A) BATH assay. The percentage of hydrophobicity of wild-type and spsA mutant spores was calculated as previously reported (2). The data are averages from three independent experiments performed with spores prepared independently, and the difference is statistically significant (*, P = 0.0195). (B) Clumping assay. Spores of the wild type (black squares) and spsA (gray squares) and sps (white squares) mutants were suspended in distilled water, and the decrease of optical density was monitored over time. The same amount of purified spores (7.5 × 107 ± 0.1 × 107,corresponding to an OD580 of 0.5) of each strain was used. The data are averages from three independent experiments performed with spores prepared independently, and the difference between spores of the sps mutant and those of the other two strains is statistically significant (P = 0.0009). (C to E) Optical microscopy fields (60× lens) of purified spores of the wild type (C) and spsA (D) and sps (E) mutant strains. Boxes report parts of the same microscopy fields observed by a 100× immersion lens. A size bar is shown for each picture.