FIG 2.
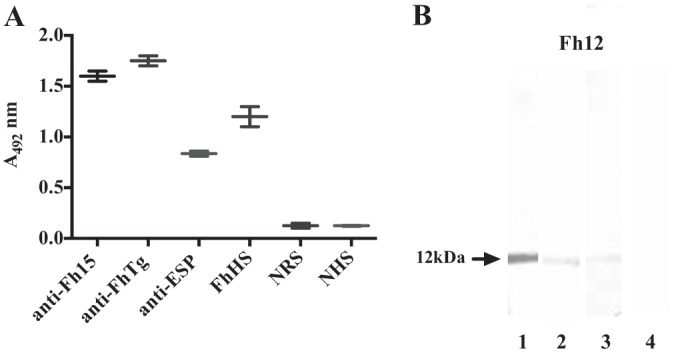
Immunoreactivity of native Fh12 as determined by ELISA and Western blotting. Purified F. hepatica fatty acid binding protein (Fh12) was assessed against different antisera raised in rabbits. (A) The ELISA plates were coated with 15 μg/ml Fh12. Sera were diluted 1:400 in PBS containing 0.05% Tween 20 (PBST), and the anti-rabbit IgG or anti-human IgG peroxidase conjugates were used diluted 1:5,000 in PBST. Fh12 was tested against an antiserum prepared against recombinant F. hepatica FABP (anti-Fh15), an antiserum prepared against F. hepatica tegumental antigen (anti-FhTg), an antiserum against F. hepatica excretory-secretory products (anti-ESP), 6 human sera obtained from patients with chronic fascioliasis (FhHS), 6 negative rabbit sera (NRS), and 6 sera from healthy subjects (NHS). The experiment was replicated three times and the results expressed as the mean absorbance at 492 nm ± standard deviation (SD). (B) Purified Fh12 was analyzed by 12.5% SDS-PAGE and electrotransfer to a nitrocellulose membrane, which was cut into strips that were incubated with anti-Fh15 (lane 1), anti-FhTg (lane 2), anti-ESP antiserum (lane 3), and negative rabbit serum (lane 4) diluted 1:100 in PBST. After successive washes to eliminate excess antibody and addition of the anti-rabbit IgG peroxidase conjugate (diluted 1:2,000 in PBST), immunoblots were revealed by incubation with diaminobenzidine as a chromogenic substrate. The arrow indicates the presence of the 12-kDa polypeptide detected in each immunoblot.
