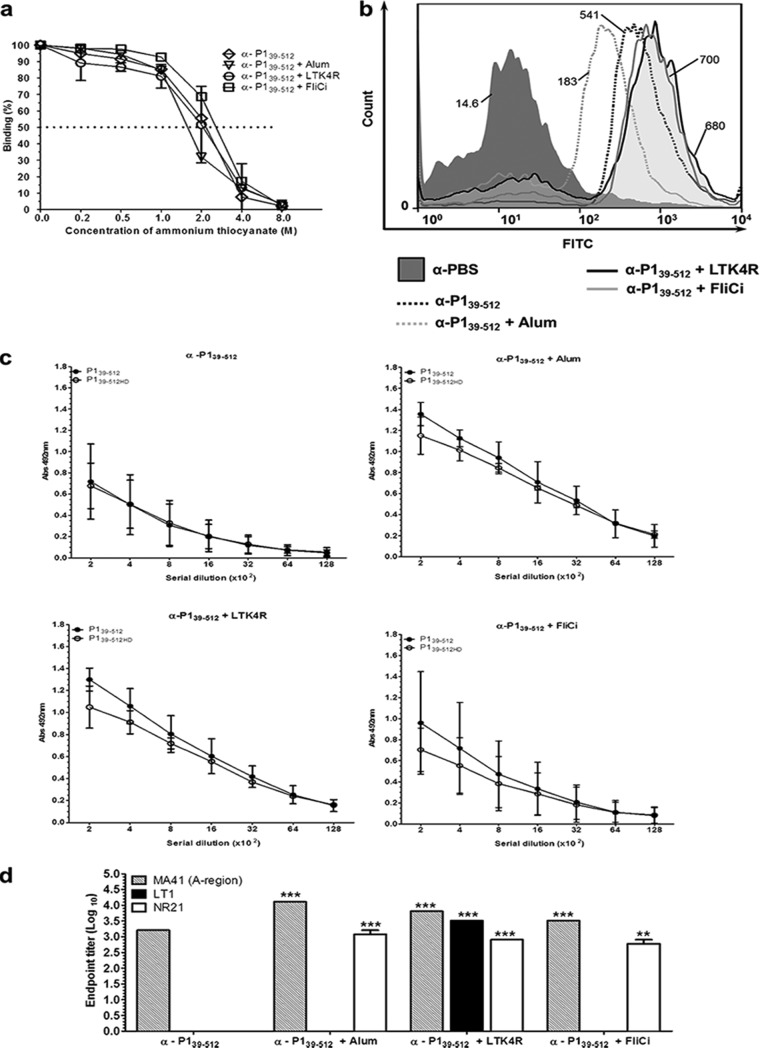
FIG 4.
Determination of avidity, reactivity with the S. mutans cell surface, and epitope specificity of antibodies raised in mice immunized with P139–512 and the different vaccine adjuvants. (a) Antibody avidity was assessed by normalizing pooled serum samples from each group to achieve an absorbance of 1 on ELISA plates coated with P139–512 and tested for dissociation with increasing amounts of ammonium thiocyanate, as described in Materials and Methods. The dotted line indicates 50% dissociation of antigen-antibody complexes. (b) Determination of reactivity of anti-P139–512 antibodies with native P1 protein on the surface of S. mutans cells by FACS analysis. Immunization groups are indicated. The median bacterial fluorescence intensity is indicated. (c) Determination of reactivity of serum samples with recombinant P139–512 protein by ELISA. P139–512 was used as a solid-phase antigen in two forms: untreated or heat denatured (P139–512HD). Immunization groups are indicated at the top. (d) Reactivity of anti-P139–512 antibodies with other truncated P1 fragments (Fig. 1a). Recombinant proteins representing the A region (MA41), the segment intervening between the A- and P-repeat regions (LT1), and a polypeptide representing LT1 fused to post-P-region sequence (NR21) were used as solid-phase-bound antigens in ELISAs. All experiments were performed with serum pools collected from mice following the third vaccine dose. Results are represented as endpoint titer values. Statistically significant differences were determined in comparison to serum samples from mice immunized with P139–512 without adjuvant (**, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001).