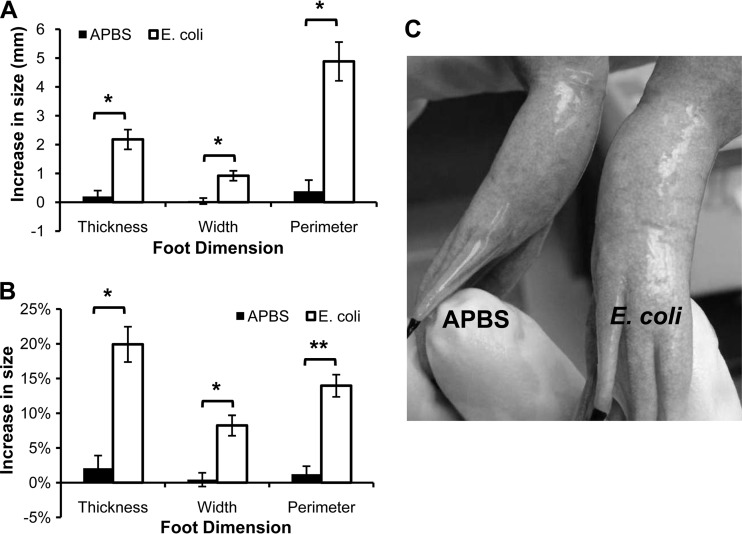
FIG 3.
Intramuscular injection of killed E. coli into the foot of X. laevis induces inflammatory swelling after 24 h. E. coli injections induced significantly greater swelling than buffer (APBS) controls (*, P < 0.01; **, P < 0.001 [paired Student's t test; alpha set to 0.017 for multiple tests]). The data show the mean (± the SEM) increase in actual size (A) or percent increase (B) in foot size compared to each foot's measurement before injection from both feet of six frogs. (C) Representative photograph of an individual 24 h after injection of APBS in the right foot and of killed E. coli into the left foot (the picture shows the ventral side of the frog).