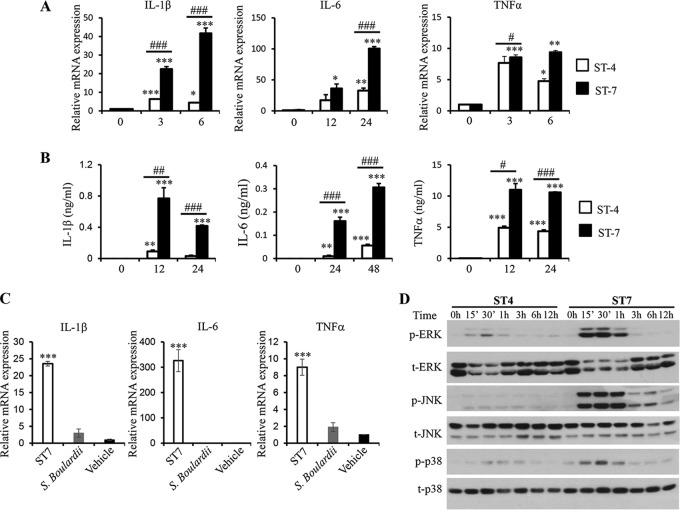
FIG 2.
Blastocystis ST-7 (B) induces stronger proinflammatory cytokine expression and MAPK activation in murine macrophages than ST-4 (WR1). RAW264.7 cells were incubated with lysates of either Blastocystis ST-4 (WR1) or ST-7 (B) at MOIs of 20 and 10, respectively. (A) mRNA levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and GAPDH in macrophages were measured by qRT-PCR. The results are normalized to GAPDH and expressed as the mean fold change relative to the 0-h time point, which is set at 1. (B) The concentrations of IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-1β in the culture supernatants of RAW264.7 cells were measured by ELISA. Each value represents the mean and standard deviation from at least 3 individual experiments. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.005 (representing a statistically significant difference compared to the negative control). #, P < 0.05; ##, P < 0.01; ###, P < 0.005 (representing a statistically significant difference between Blastocystis ST-4 and ST-7). (C) S. boulardii lysate does not induce inflammatory cytokine expression in macrophages. RAW264.7 cells were incubated with lysate of either Blastocystis ST-7 (B) (MOI, 10) or S. boulardii (MOI, 20). The mRNA levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and GAPDH in macrophages were measured by qRT-PCR. (D) Representative Western blots of MAPK activation in RAW264.7 cells in response to ST-4 (WR1) or ST-7 (B) lysate stimulation. Cells were lysed and were processed by SDS-PAGE. Membranes were then blotted with phospho-ERK (p-ERK), total ERK (t-ERK), phospho-JNK, total JNK, phospho-p38, and total p38 antibodies. Each blot is representative of three separate experiments.