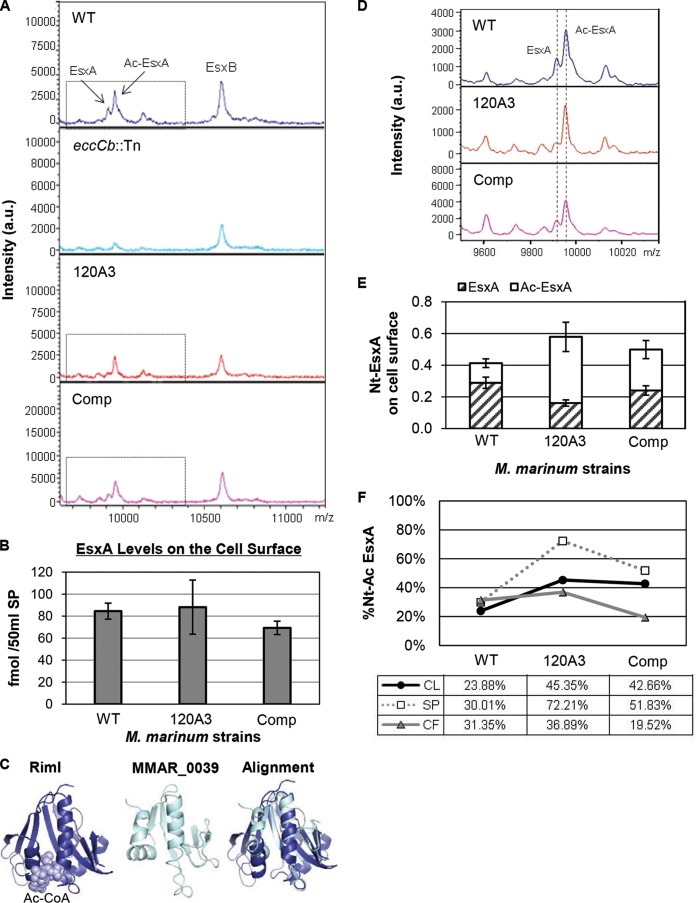
FIG 5.
The N-α-terminal acetylation of EsxA, but not export to the cell surface, is altered in the 120A3 strain. (A) Whole-colony MALDI assay to measure EsxA and EsxB export to the cell surface. Two MALDI peaks represent unacetylated EsxA and N-α-terminally acetylated EsxA (Ac-EsxA). The eccCb::Tn strain served as a control for lysis. au, arbitrary units. (B) Absolute levels of EsxA from surface proteins from M. marinum WT, 120A3, and complemented strains. Quantification was determined by LC-MS/MS (MRM-based) analysis of tryptic digests with the addition of stable isotope dilution of peptides from each protein. EsxA values shown are normalized to GroES values (see Fig. S4 in the supplemental material). Standard error is shown from triplicate analyses. There is no statistically significant difference between the levels of EsxA on the surface for all three strains as determined by a one-way ANOVA (F2,6 = 2.161, P = 0.1964). (C) Model of the Salmonella RimI NAT bound to acetyl-CoA based on the structure by Vetting et al. (44) generated using PyMOL (78). The Phyre 2 model MMAR_0039 was generated using PyMOL. The alignment of RimI and MMAR_0039 was performed using FatCat (57) and modeled using PyMol. (D) MALDI peaks for unacetylated EsxA and acetylated EsxA (Ac-EsxA) (dotted lines) generated from SPs from M. marinum strains grown on Sauton's agar. The peaks are enlarged versions of the peaks boxed in panel A for emphasis. (E) Quantitation of unacetylated and N-α-terminally acetylated EsxA (Nt-EsxA) from surface proteins from M. marinum WT, 120A3, and complemented strains using MRM analysis. The average area ratio normalized to GroES is shown. Standard error is shown from triplicate analysis. The statistical significance of the differences between the WT and 120A3 strains, as well as the WT and complemented strains, were determined using Student's t test and are listed in the text. (F) Percentage of the EsxA peptides that were N-α-terminally acetylated (%Nt-Ac) in the CL, SP, and CF fractions generated from M. marinum WT, 120A3, and complemented strains. Percent acetylation was calculated as follows: (area ratio of N-α-terminally acetylated peptide)/(area ratio of N-α-terminally acetylated peptide + area ratio of unacetylated N-terminal peptide) × 100. The statistical significance of the differences in percent acetylation were determined using Student's t test; the P values are indicated in the text.