FIG 2.
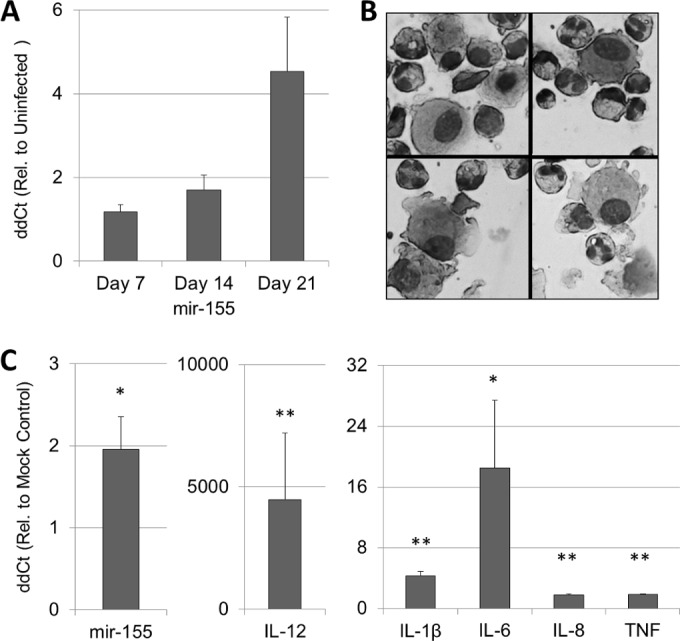
S. pneumoniae induces mir-155 in the murine nasopharynx, as well as in resident cells of the human upper respiratory tract. (A) WT mice were colonized intranasally with S. pneumoniae (P1121), and nasopharyngeal mir-155 expression was measured by quantitative PCR. n = 3 to 6 per time point. Sputum leukocytes (presented in panel B) were stimulated with S. pneumoniae or mock stimulated with PBS for 16 h; this was followed by the assessment of mir-155 and cytokine gene expression (C). n = 3 or 4 per gene. Rel., relative. Statistical significance was determined by paired t test on log-transformed CT values. **, P < 0.01; *, P < 0.05.
