FIG 3.
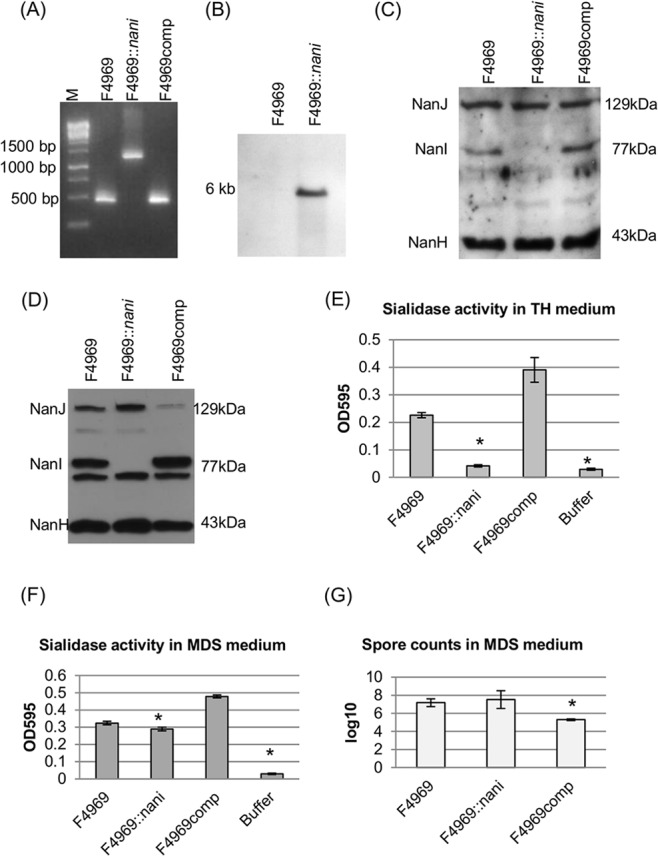
Creation and characterization of the isogenic F4969 nanI null mutant F4969::nanI and NanI complemented strains in both TH and MDS medium. (A) nanI internal PCR analysis for wild-type strain F4969, the nanI null mutant strain F4969::nanI, and nanI-complemented strain F4969comp. Without intron insertion, the PCR product amplified from the wild-type strain was ∼470 bp. With an ∼900-bp intron insertion, the PCR product amplified from the isogenic nanI null mutant strain was 1,370 bp using the same primers. The complemented strain, with the wild-type nanI gene, supported amplification of a PCR product matching the small band amplified from the wild-type strain. M, 100-bp DNA ladder (purchased from Fisher Scientific). (B) Southern blot analysis of an intron-specific probe with DNA from wild-type F4969 or the nanI null mutant strain F4969::nanI. DNA from both strains was digested with EcoRI and electrophoresed on a 1% agarose gel prior to blotting and hybridization with an intron-specific probe. Sizes of DNA fragments in kb are shown on the left. (C) Western blot analyses for sialidase expression by wild-type F4969, nanI null mutant, or nanI complemented strains using TH overnight culture supernatants. Sizes of proteins in kDa are shown on the right. (D) Western blot analyses for sialidase expression by wild-type F4969, the nanI null mutant, and the nanI complemented strain using overnight MDS culture supernatants. Sizes of proteins in kDa are shown on the right. (E) Sialidase activity analyses for wild-type F4969, the nanI null mutant, or the nanI complemented strain using overnight (∼16-h) TH culture supernatants. All the results show the averages of three repetitions; the error bars indicate the SD. Statistical analysis (Friedman test) showed that sialidase activity was significantly different for the wild-type and mutant or complemented and mutant strains (P < 0.05). (F) Sialidase activity analyses for wild-type F4969, nanI null mutant, or nanI complemented strains using overnight (∼16-h) MDS culture supernatants. All results show the averages of three repetitions; the error bars indicate the SD. The statistical analysis (Friedman test) showed that sialidase activity has a significant difference between the mutant and the complemented strains (P < 0.05). (G) Heat-resistant spore formation by F4969, the nanI null mutant strain, or nanI complemented strain. The bacteria were grown in MDS overnight at 37°C and then heat shocked for 20 min at 70°C. After a 10-fold serial dilution with distilled water, the heat-shocked cultures were then plated onto BHI agar plates and grown overnight at 37°C for colony counting. All results show the averages of three repetitions; the error bars indicate the SD. Statistical analysis (Friedman test) showed that the number of spores was significantly different in the complemented and mutant strains (P < 0.05).
