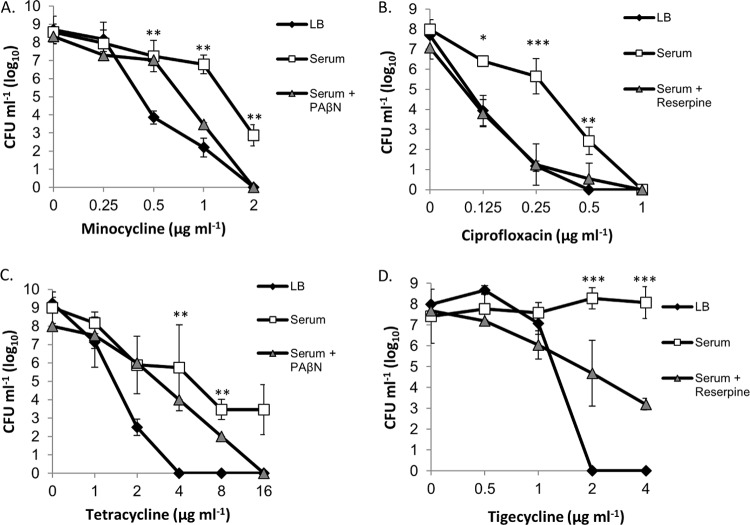
FIG 1.
Antimicrobial effects of minocycline, ciprofloxacin, tetracycline, and tigecycline toward LB- and serum-grown A. baumannii. (A) Plotted are the CFU of strain 98-37-09 following incubation in LB or serum (with/without the efflux pump inhibitor PAβN) supplemented with 0 to 2 μg ml−1 of minocycline. (B) CFU of strain 98-37-09 following incubation in LB or serum (with/without the efflux pump inhibitor reserpine) supplemented with 0 to 1 μg ml−1 of ciprofloxacin. (C) CFU of strain 98-37-09 following incubation in LB or serum (with/without the efflux pump inhibitor PAβN) supplemented with 0 to 16 μg ml−1 of tetracycline. (D) CFU of strain 01-12-05 after incubation in LB or serum (with/without the efflux pump inhibitor reserpine) supplemented with 0 to 4 ml−1 of tigecycline. The mean CFU ± standard deviations are plotted on the y axis, and antibiotic concentration is indicated on the x axis; the asterisks indicate statistically significant differences in CFU between growth in LB and serum (Student's t test; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001).