FIGURE 2.
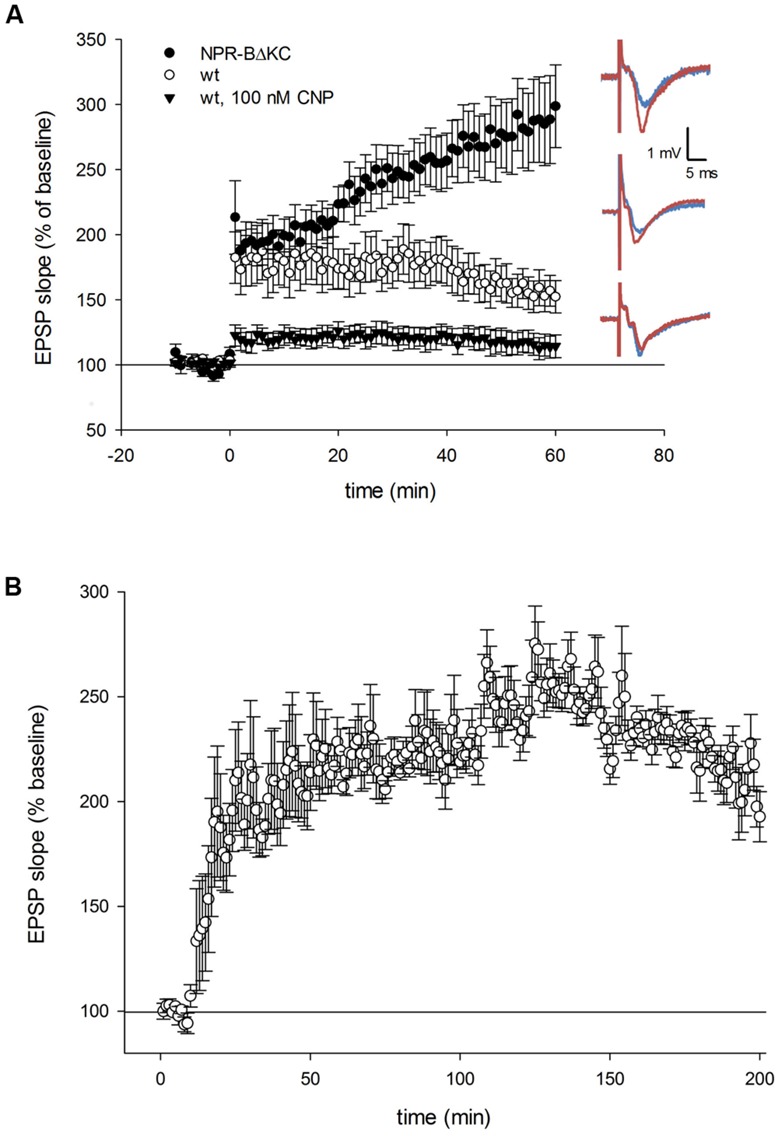
(A) Time course of the relative changes in the excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) slope expressed in % of baseline stimulation induced by 100 Hz HFS for 1 s in hippocampal slices from NPR-BΔKC, from wild type rats (wt) and from wild type slices incubated with the NPR-B agonist CNP (100 nM). Sample traces of the electrically evoked EPSPs for the NPR-BΔKC, wild type slices, and wild type slices incubated with 100 nM CNP are shown on the right, and were recorded 10 min before and 60 min following high frequency stimulation (HFS, 100 Hz for 1 s). Note that LTP was more strongly expressed in slices from NPR-BΔKC rats (black circles) compared to wt (white circles). Bath application of 100 nM CNP (black triangles) caused attenuation of LTP. (B) The increase of the EPSP slope in NPR-BΔKC rats reaches saturation levels at 285% of baseline stimulation after 120 min. EPSPs decrease slowly to ∼200% of baseline stimulation after 180 min.
