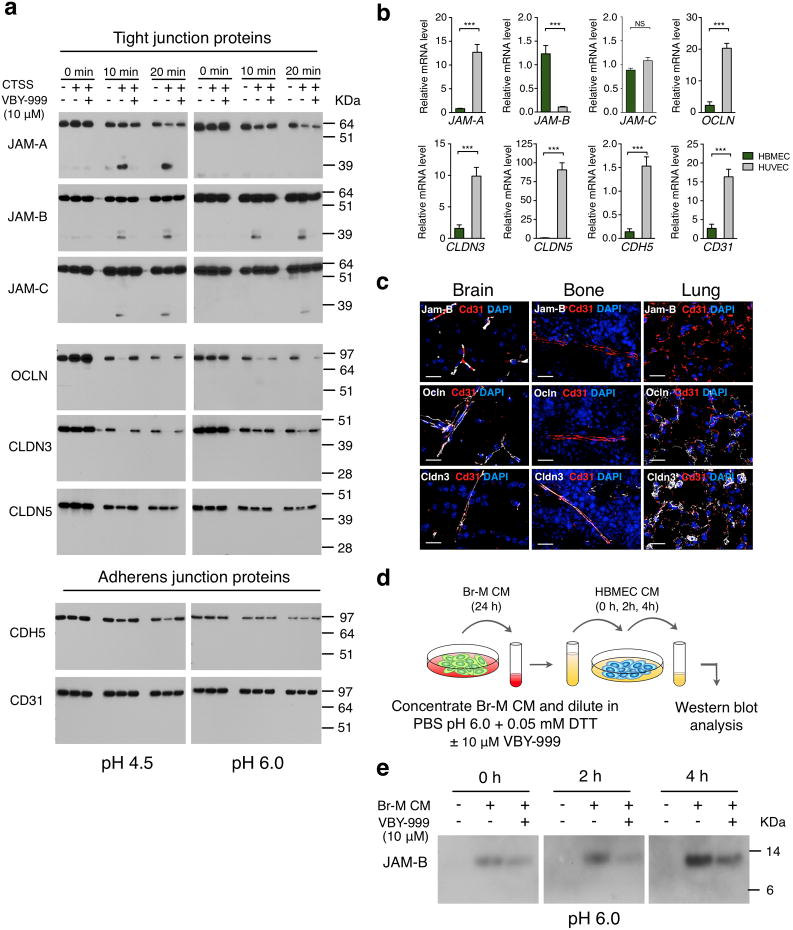
Figure 7. Cathepsin S cleaves tight junction proteins that regulate blood-brain barrier integrity.
(a) Western blot analysis of CTSS-mediated cleavage of recombinant tight junction proteins (junctional adhesion molecules (JAM)-A, -B and -C, occludin (OCLN), claudins (CLDN)-3 and-5), and adherens junction proteins cadherin 5 (CDH5) and CD31 for the indicated time points at pH 4.5 and pH 6.0 in the presence or absence of the cathepsin S-specific inhibitor VBY-999. VBY-999 was used at 10 μM, a concentration that efficiently inhibits cathepsin S. (b) mRNA expression of the tight junction and adherens junction molecules in HUVECs and HBMECs (n=9 samples for each cell line). All assays were run in triplicate and gene expression was normalized to B2M. Expression is depicted relative to expression in HBMECs. (c) Representative images of control brain, bone, and lung sections stained for the tight junction proteins Jam-B, Ocln or Cldn 3 (white), with CD31 (red) to visualize blood vessels. DAPI was used as a nuclear counterstain. Images are representative of 3 independent specimens. (d) Schematic of the cell-based cleavage assay. (e) Western blot analysis showing increased JAM-B in HBMEC-conditioned media (CM) after incubation with Br-M cell CM for the indicated time points. Addition of the cathepsin S specific inhibitor VBY-999 (10 μM) resulted in reduced accumulation of JAM-B in HBMEC CM at the indicated time points. Incubation with PBS pH 6.0, 0.05 mM DTT served as a control for baseline JAM-B shedding of HBMEC. Scale bar indicates 20 μm. Graphs represent mean + s.e.m. P values were obtained using two-tailed unpaired t-test. NS = not significant, ***P<0.001. Each western blot shows the representative result of three independent experiments. Uncropped images of blots are shown in Supplementary Fig. 9.