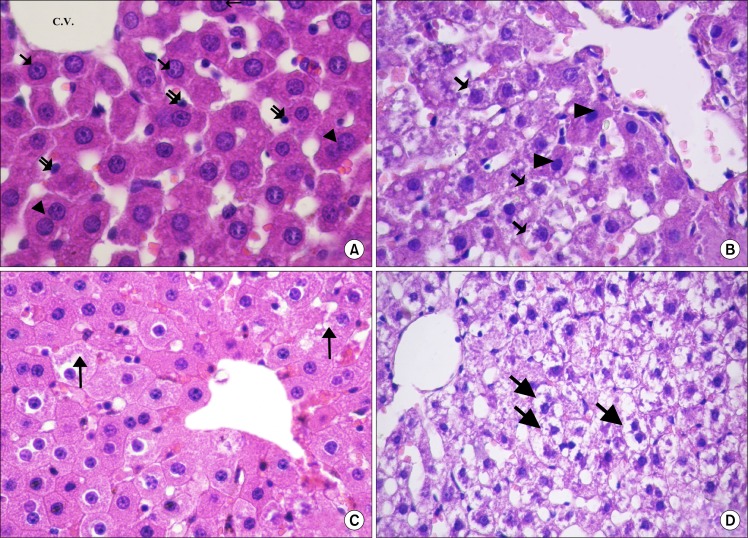
Fig. 1.
(A) Showing radiating cords of hepatocytes from the central vein (C.V.). The hepatocytes have central, rounded, vesicular nuclei (↑) and acidophilic cytoplasm. Some of the cells appear bi-nucleated (▲). Notice the lining cells (
 ) of the blood sinusoids (control H and E. ×720). (B) Most of the hepatocytes are vacuolated (
) of the blood sinusoids (control H and E. ×720). (B) Most of the hepatocytes are vacuolated (
 ). Few hepatocytes appear with acidophilic cytoplasm and deeply stained nuclei (▲) (CCL4 alone group. H and E. ×560). (C) Most of the hepatocytes have granular acidophilic cytoplasm and vesicular nuclei. Few cells show cytoplasmic vacuolation (↑) (CCL4/MSCs group. H and E. ×560). (D) Showing highly vacuolated hepatocytes with deeply stained nuclei (↑) (CCL4/Recovery group, H and E. ×400).
). Few hepatocytes appear with acidophilic cytoplasm and deeply stained nuclei (▲) (CCL4 alone group. H and E. ×560). (C) Most of the hepatocytes have granular acidophilic cytoplasm and vesicular nuclei. Few cells show cytoplasmic vacuolation (↑) (CCL4/MSCs group. H and E. ×560). (D) Showing highly vacuolated hepatocytes with deeply stained nuclei (↑) (CCL4/Recovery group, H and E. ×400).