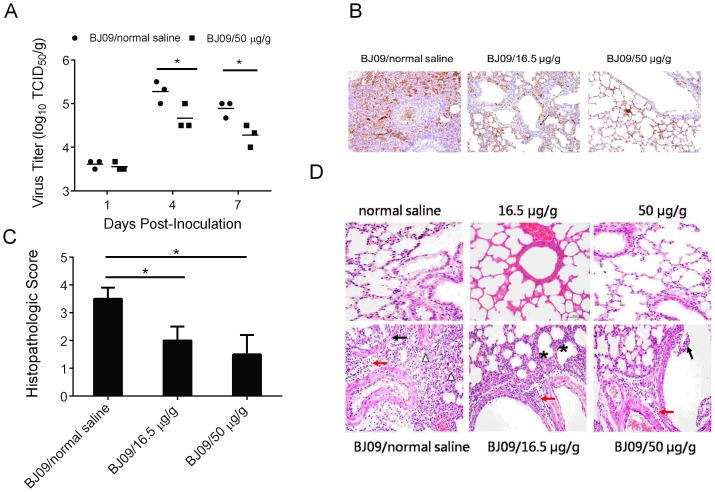
Figure 4. Cryptoporus volvatus extract inhibits H1N1 influenza virus replication in vivo, and reduces severity of pathological changes.
(A) Virus replication in lung of mice. Titers of virus recovered from the supernatant of homogenized lung at day 1, 4, and 7 p.i. are shown. (B) Immunohistochemistry analysis of the lung of influenza virus-infected mice treated with normal saline or the extract. Scale bars, 100 µm. (C) Lung histological grading of virus-infected mice treated with normal saline or the extract (5 sections from each lung, and 3 mice per group). (D) Representative of histopathological changes in H&E stained lung tissues from mice sacrificed at day 4 p.i.. normal saline (negative control group); 50 µg/g (extract control group), no histopathology lesion; BJ09/normal saline (virus infection control group): severe desquamation and droplet of bronchial mucosa (↑), massive immune cell and red blood cell infiltrates around bronchi and blood vessels (red arrow), and inflammatory cells within alveolar spaces (△); BJ09/16.5 µg/g (virus infection and treated with low-dosage extract group): a small number of immune cell infiltrates around bronchi and blood vessels (red arrow), and alveolar wall thickened (*); BJ09/50 µg/g (virus infection and treated with high-dosage extract group): a small number of immune cell infiltrates around bronchi and blood vessels (red arrow), and mild desquamation of bronchial mucosa (↑). (Scale bar: 50 µm). Data are presented as mean ±SD. Statistical significance was analyzed by Student's t test; *P<0.05; **P<0.01.