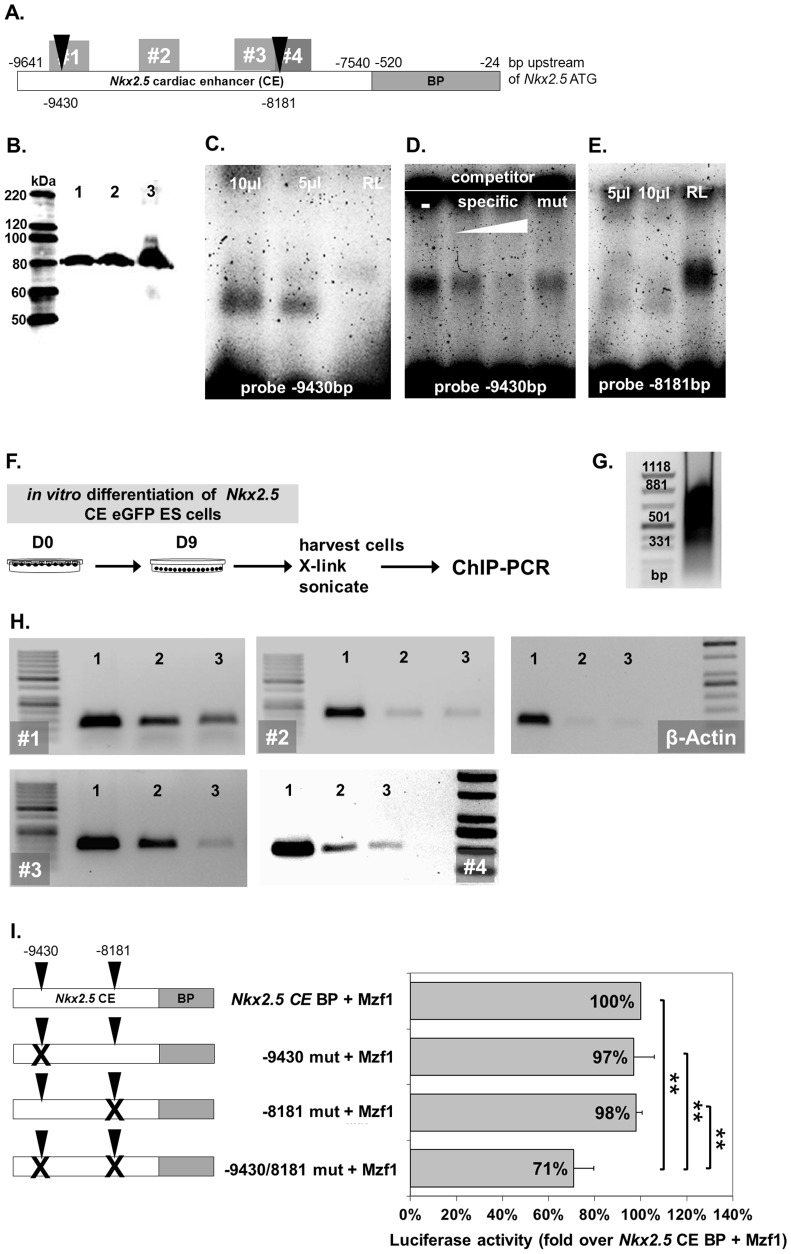
Figure 2. Direct binding of Mzf1 to the Nkx2.5 cardiac enhancer in vitro and in vivo.
A. Locations of analyzed described Mzf1 binding motifs in the Nkx2.5 CE [8], [11] (black triangles) and primer sets #1-#4 for ChIP PCR (grey rectangles with numbers). B. In vitro translated Mzf1 protein from the flag-Mzf1-pcDNA3.1 confirmed by an anti-flag antibody in western-blotting (lane 3). As a control whole cell lysates from 293 cells transfected with the flag-Mzf1-pCDNA3.1 plasmid were used (lane 1 & 2). The predicted molecular weight for Mzf1 is 84 kDa. C. Different amounts of in vitro translated Mzf1 (10µl, 5µl) bound to the Nkx2.5 CE at the binding motif corresponding to zinc fingers 5-13 (black triangle at position -9430 bp) [8], [11] in an electromobility shift assay (EMSA). Unprogrammed reticulocyte lysate (RL) was applied as a control. D. Competition assays with untagged mutant (mut, 10-fold excess) and specific probes (10- and 50-fold excess) were performed to ensure specificity. E. In vitro binding to the motif corresponding to zinc fingers 1-4 (at position −8181 bp) [8], [11] by EMSA could not be confirmed. Different amounts of in vitro translated Mzf1 (10µl, 5µl) were used. Unprogrammed reticulocyte lysate (RL) was applied as a control. F. Experimental set-up for ChIP assays. Chromatin was isolated from day nine differentiated Nkx2.5 CE eGFP ES cells. G. Chromatin was sheared by sonication to obtain fragment sizes between 250 and 1000 bp. H. ChIP-PCR on purified chromatin using a polyclonal anti-Mzf1 and an isotype-matched control antibody. Lane 1: 4% sonicated input chromatin. Lane 2: Chromatin precipitated with the Mzf1 antibody. Lane 3: Chromatin precipitated with an IgG matched control antibody. I. Effect of mutating two Mzf1-binding sites at positions −9430 bp and -8181 bp in the Nkx2.5 CE on luciferase activity by Mzf1 in HEK 293 cells (** = p <0.01).