Fig. 2.
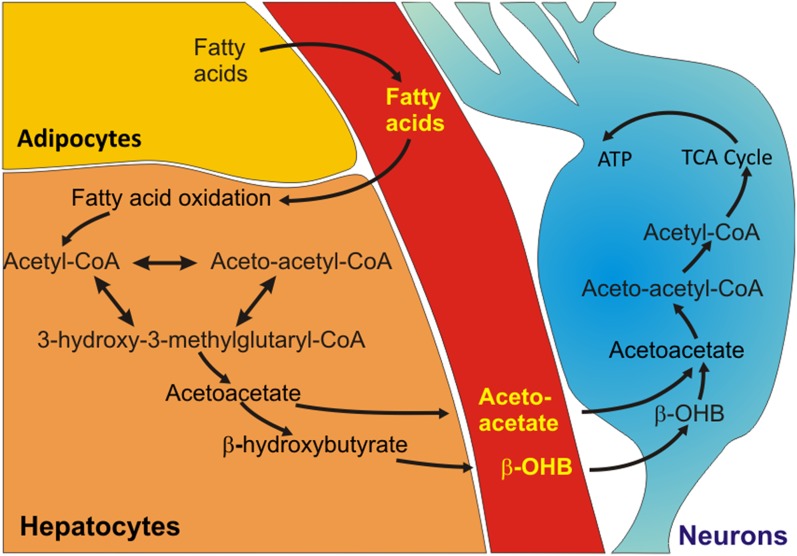
A metabolic shift to ketogenesis that occurs with fasting bolsters neuronal bioenergetics. Liver glycogen stores are typically depleted within 10–12 h of fasting, which is followed by liberation of fatty acids from adipose tissue cells into the blood. The fatty acids are then transported into liver cells where they are oxidized to generate Acetyl-CoA. Acetyl-CoA is then converted to 3-hydroxy-3-methylgluaryl-CoA, which is in turn used to generate the ketones acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate (β-OHB). The ketones are released into the blood and are transported into various tissues, including the brain, where they are taken up by neurons and used to produce acetyl-CoA. Acetyl-CoA enters the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle to generate ATP.