Fig. 2.
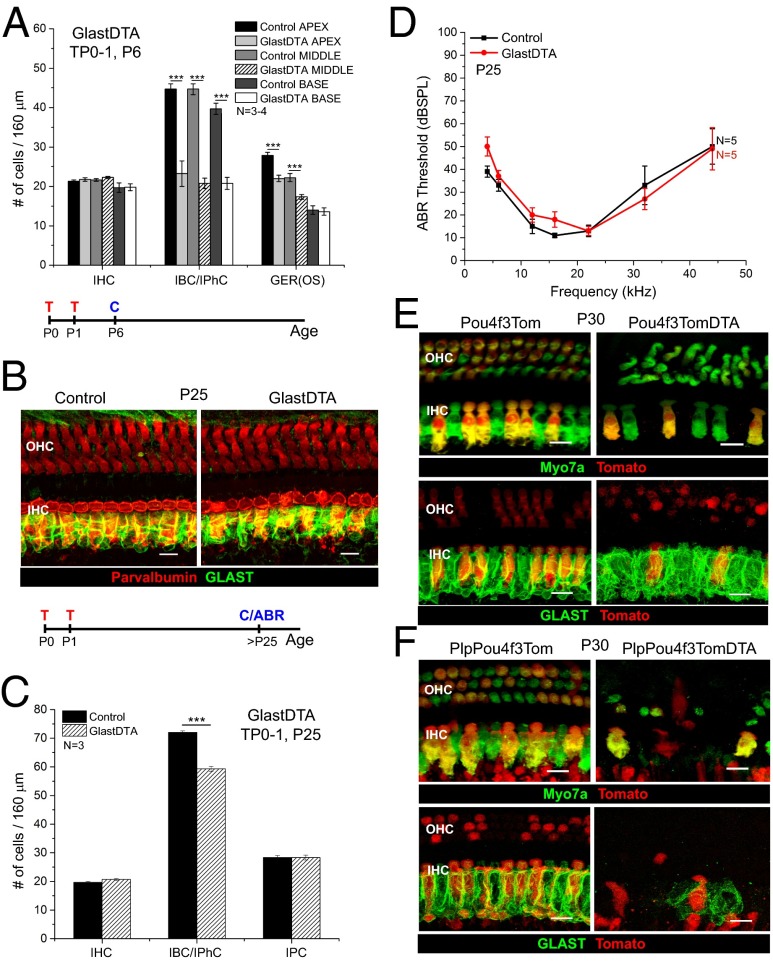
GER cells and HCs are important for IBC/IPhC replacement after neonatal ablation. (A) Quantification of the number of IHC, IBC/IPhC, and GER cells in 160-μm regions of each turn of the cochleae in GlastDTA and control mice at P6 (mean ± SEM, n = 3–4). GER(OS), GER cells were counted in optical cross-sections taken along the 160-μm regions of each turn. (B) Representative optical projections of whole mounts from the apical turn of the cochleae of GlastDTA and control mice induced with tamoxifen at P0 and P1; cochleae were analyzed at P25 showing parvalbumin+ HCs (red) and GLAST+ IBCs/IPhCs (green). The timelines below A and B show the protocol of tamoxifen induction (T), cochlea collection (C), and ABR measurement (ABR) used in each figure of these mouse models. (C) Quantification of the number of cells of each subtype present in the IHC area of the apical organ of Corti in GlastDTA and control mice at P25 (mean ± SEM, n = 3). IHCs and SCs were counted in 160-μm sections in the apical turn of the organ of Corti. SCs were counted as the number of Sox2+ nuclei in the specific locations of the cell type in control samples. (D) ABR thresholds from P25 GlastDTA and control mice (mean ± SEM, n = 5). No statistical differences in ABR thresholds were observed in GlastDTA and control mice. (E) Representative optical projections of whole mounts from the apical turn of the cochleae of P30 Pou4f3Tom and Pou4f3TomDTA mice showing IHC and OHC loss when the DTA allele is present (Upper) and preservation of GLAST+ IBCs/IPhCs after HC ablation in Pou4f3TomDTA mice (Lower). (F) Representative optical projections of whole mounts from the apical turn of the cochleae of PlpPou4f3Tom and PlpPou4f3TomDTA mice at P30 showing loss of HCs and absence of GLAST+ IBC/IPhC replacement after neonatal ablation. (Scale bars: 10 μm.) ***P < 0.001.