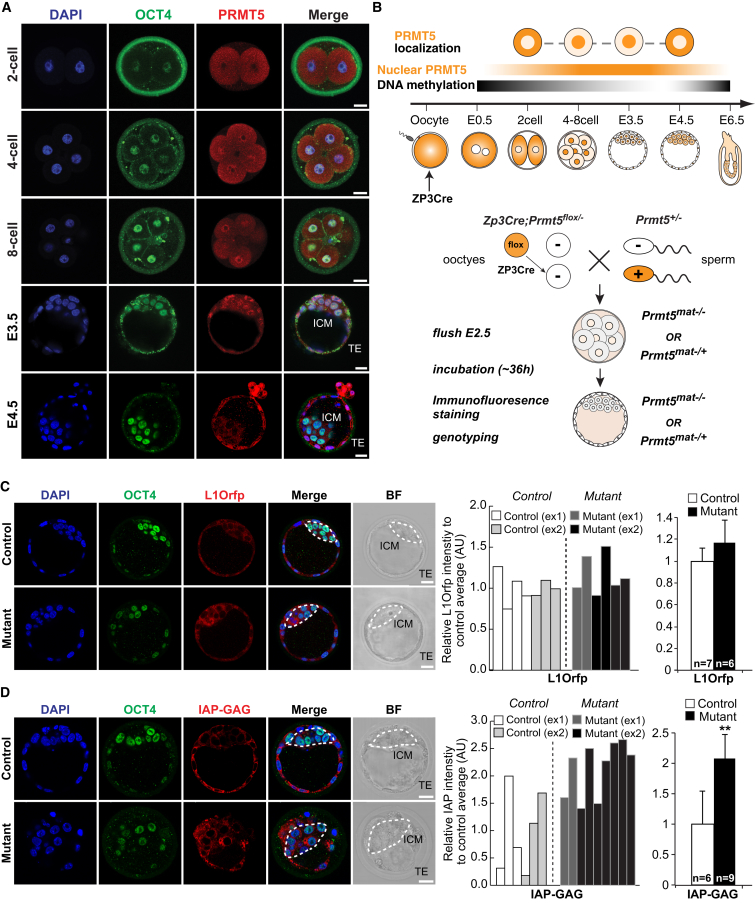
Figure 6.
Prmt5 Is Required for the Suppression of TEs in Preimplantation Embryos
(A) IF staining of OCT4 (green) and PRMT5 (red) in wild-type two-cell to blastocyst-stage preimplantation embryos (stages are indicated). Note that PRMT5 is detected in the nucleus from four-cell-stage embryos. TE, trophectoderm; ICM, inner cell mass; scale bars, 20 μm.
(B) Schematic diagram of the subcellular localization of PRMT5 (shown in orange) and the level of nuclear PRMT5 during preimplantation development (top). Zp3Cre is expressed during oocyte maturation. The mating scheme shows how the maternal-zygotic Prmt5 knockout embryos were generated followed by the experimental outline (bottom).
(C) IF staining of OCT4 (green) and L1Orf1p (red) in control (Prmt5mat−/+) and maternal-zygotic Prmt5 mutant (Prmt5mat−/−) preimplantation embryos. The dashed line indicates the ICM region. Scale bars, 20 μm. The fluorescence intensity of L1Orf1p in preimplantation embryos was determined using seven control and six mutant embryos. The data are from two independent experiments, and the relative L1Orf1p intensity of each embryo compared to the mean intensity of control embryos is shown. The right graph shows the mean intensity ± SD of all embryos. n, number of embryos.
(D) IF staining of OCT4 (green) and IAP-GAG (red) in control (Prmt5mat−/+) and maternal-zygotic Prmt5 mutant (Prmt5mat−/−) preimplantation embryos. The ICM region is indicated by the dashed line. Scale bars, 20 μm. The fluorescence intensity of IAP-GAG in preimplantation embryos was determined in six control embryos and nine mutant embryos. The data are from two independent experiments, and the relative IAP-GAG intensity of each embryo compared to the mean intensity of control embryos is shown. The right graph shows the mean intensity ± SD of all embryos. n, number of embryos; significance was tested with the Student’s t test, ∗∗p < 0.01.
See also Figure S6.