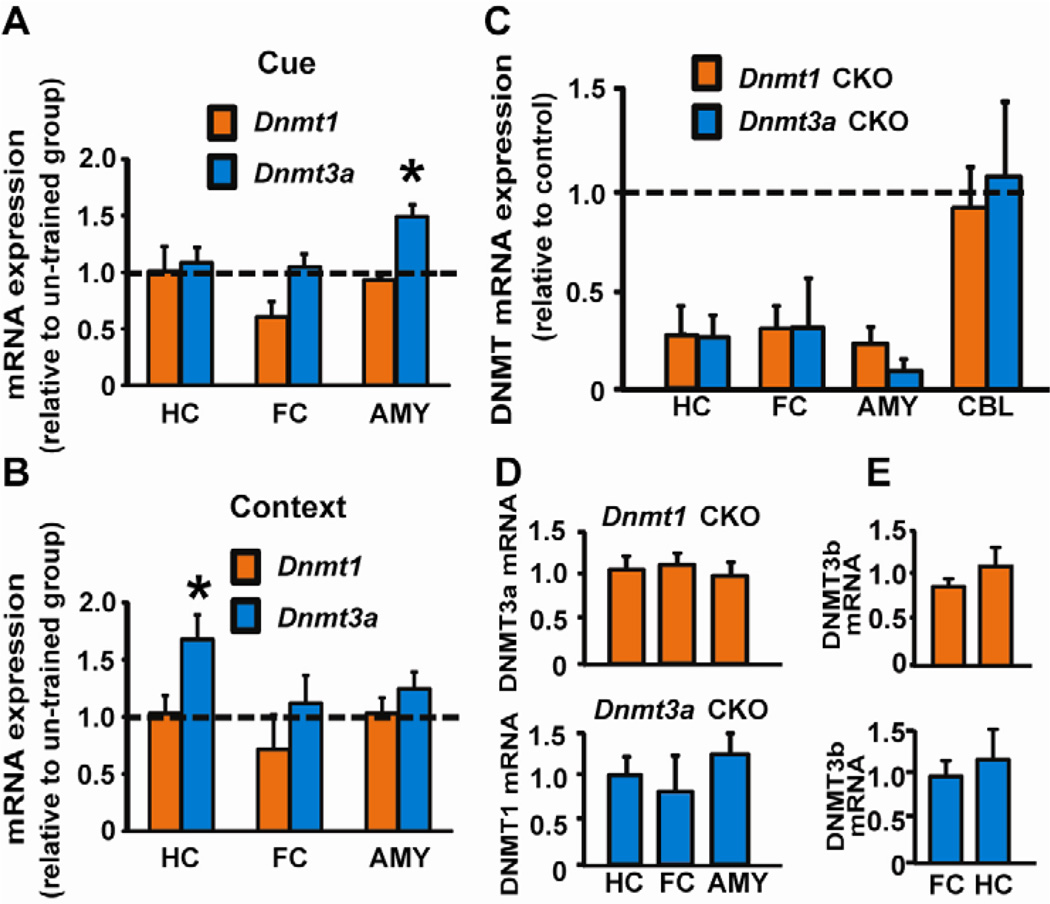
Fig. 1.
Dnmt1 and Dnmt3a mRNA expression in mouse brain. (A) After training in cued fear conditioning Dnmt3a expression was increased in the amygdala (AMY) of C57BL/6 mice relative to un-trained mice [t(8) = 3.219, p = 0.012]. A trend (p = 0.062) for reduced Dnmt1 expression was evident in frontal cortex (FC). (B) Training in contextual fear conditioning increased Dnmt3a expression in hippocampus (HC) [t(10) = 2.30, p = 0.049] with a trend in AMY (p = 0.16); Dnmt1 expression was unchanged in HC, FC, and AMY. (C) Consistent with forebrain-specific deletion, Dnmt1 or Dnmt3a mRNA was reduced in 6-week old CKOs in HC, AMY, and FC, with no change in cerebellum (CBL). (D) No compensation in Dnmt3a expression when Dnmt1 was knocked down (top panel), and vice versa (bottom panel). (E) No changes in Dnmt3b expression in Dnmt1 and Dnmt3a CKO mice (top and bottom panels, respectively) in comparison to control animals. *p < 0.05 compared with un-trained CTL (n= 4–6/group in all groups).