Figure 5.
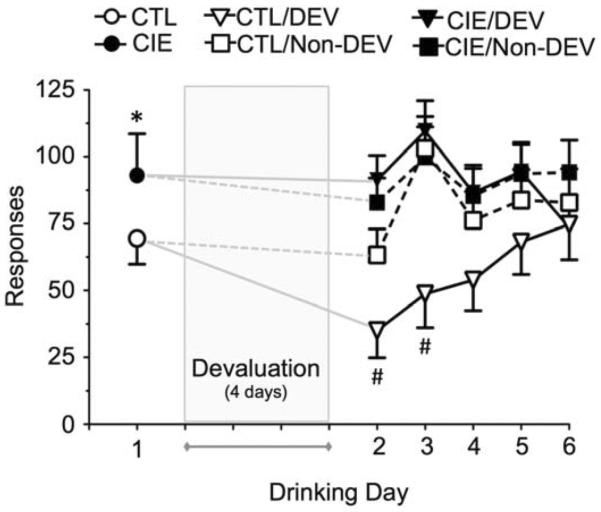
Repeated cycles of CIE promote insensitivity to devaluation of responding for ethanol. Prior to devaluation, mice subjected to 5 cycles of CIE exhibited enhanced responding for ethanol compared to the sham air-exposed controls. After ethanol or sham devaluation, responding in the air-exposed control mice was sensitive to devaluation. In contrast, CIE-exposed mice exhibited responding that was insensitive to devaluation. The * indicates significant increase of CIE versus CTL (t test, p < 0.05). The # indicates significant difference from respective non-devalued controls (ANOVA with Newman-Keuls post hoc test, p < 0.05).
