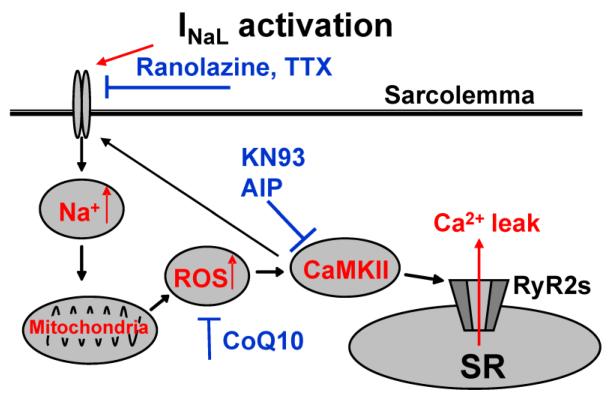
Figure 5. Proposed mechanism for INaL-mediated Na+ overload-induced disruption of myocyte Ca2+ handling.
An increase of INaL leads to an increase of [Na+]i Cytosolic Na+ overload attenuates mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake via the mitochondrial Na+/Ca2+ exchanger, thereby reducing NADPH regeneration and increasing mitochondrial ROS, ROS oxidize and activate CaMKII, resulting in phosphorylation of the CaMKII substrate RyR2 and increasing Ca2+ leak from sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR).