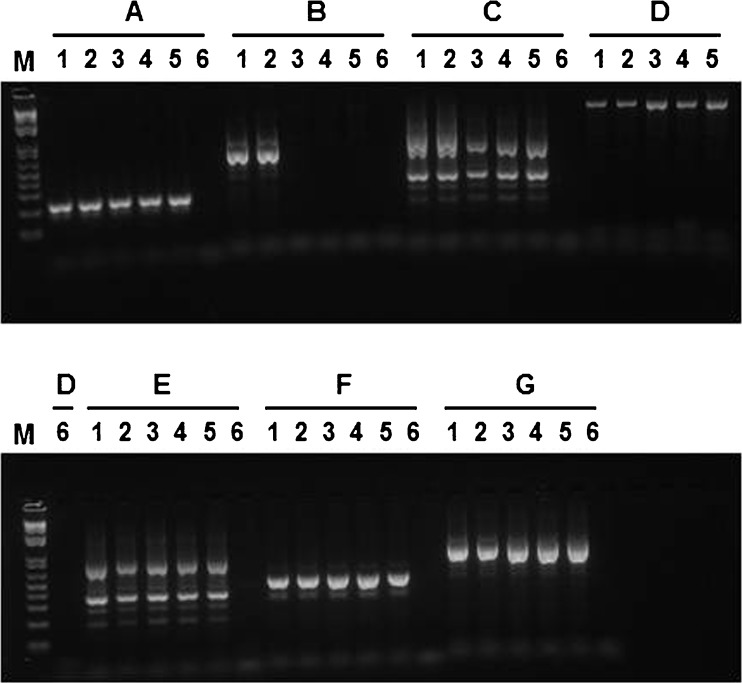
Fig. 3.
PCR screening of the genomic breakpoint. Seven pairs (A ~ G) of primers were used to amplify the putative mutation regions. Primer set A: Brca2e14-42 F & Brca2e14-242R; B: Brca2i14-216 F& Brca2i16-864R; C: Brca2i14-216 F & Brca2i16-1161R; D: Brca2i14-699 F & Brca2i16-864R; E: Brca2i14-699 F & Brca2i16-1161R; F: Brca2i14-699 F & Brca2e15-10R; and G: Brca2e16-143 F & Brca2i16-864R. Please refer to Fig. 4 for the location and sequence of each primer. The six samples from left to right were patients (1,2); sister (3,4); unrelated individual (5); H2O (6). M: 1Kb Plus DNA ladder (Invitrogen). The primer set B produced informative PCR results; an abnormal PCR product (>700 bp visualized from the agarose gel) was clearly observed in the patient's samples, but not in the samples of sister and unrelated individual