Figure 3.
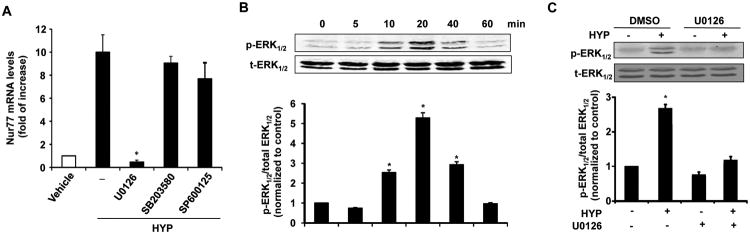
Hyperoside induces Nur77 expression through MEK pathway in RVSMCs. (A) RVSMCs were pretreated with vehicle, MEK1/2 inhibitor U0126 (20 μmol/L), the p38 MAP kinase inhibitor SB203580 (10 μmol/L), and c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitor SP600125 (50 μmol/L) for 1 hr, and then stimulated with hyperoside (HYP) (5 μmol/L) for 1 hr. The expression of Nur77 was then measured by qRT-PCR (n=5, *P<0.05 vs DMSO plus hyperoside (HYP) treatment). (B) RVSMCs were stimulated with hyperoside (HYP) (5 μmol/L) at different time points and the levels of phosphorylated ERK1/2 and total ERK1/2 were determined by Western blot analysis (n=4, *P<0.05 vs HYP at 0 min). (C) RVSMCs were pretreated with either vehicle or the MEK1/2 inhibitor U0126 for 1 hr, and then stimulated with hyperoside (HYP) (5 μmol/L) for 20 min, the levels of phosphorylated ERK1/2 and total ERK1/2 were then determined by Western blot analysis (n=4, *P<0.05 vs either DMSO or HYP plus U0126 treatment).
