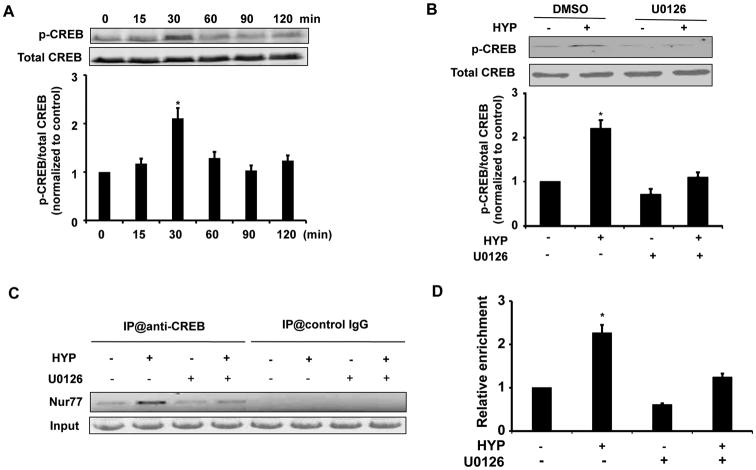
Figure 4.
CREB is involved in hyperoside-induced Nur77 expression in RVSMCs. (A) RVSMCs were stimulated with hyperoside (5 μmol/L) at different time points and the levels of phosphorylated CREB and total CREB were determined by Western blot analysis. (n=4, *P<0.05 vs hyperoside (HYP) at 0 min). (B) RVSMCs were pretreated with MEK1/2 inhibitor U0126 (20 μmol/L) for 1 hr and then stimulated with hyperoside (HYP) (5 μmol/L) for 30 min and the levels of phosphorylated CREB and total CREB were determined by Western blot analysis (n=4, *P<0.05 vs either DMSO or HYP plus U0126 treatment). (C) RVSMCs were treated or untreated with hyperoside (HYP) (5μmol/L) in the absence or presence of MEK1/2 inhibitor U0126 (20 μmol/L). PCR analysis of sheared DNA from control and hyperoside treated cells before immunoprecipitation (input) and after Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) with antibody directed against CREB or control IgG. (D) Quantitative analysis of ChiP results from three independent experiments as shown in panel C (n=4, *P<0.05 vs either DMSO or HYP plus U0126 treatment).