Figure 1. The Structure of Human B7x IgV Domain and the Epitopes Recognized by Monoclonal Antibody against B7x.
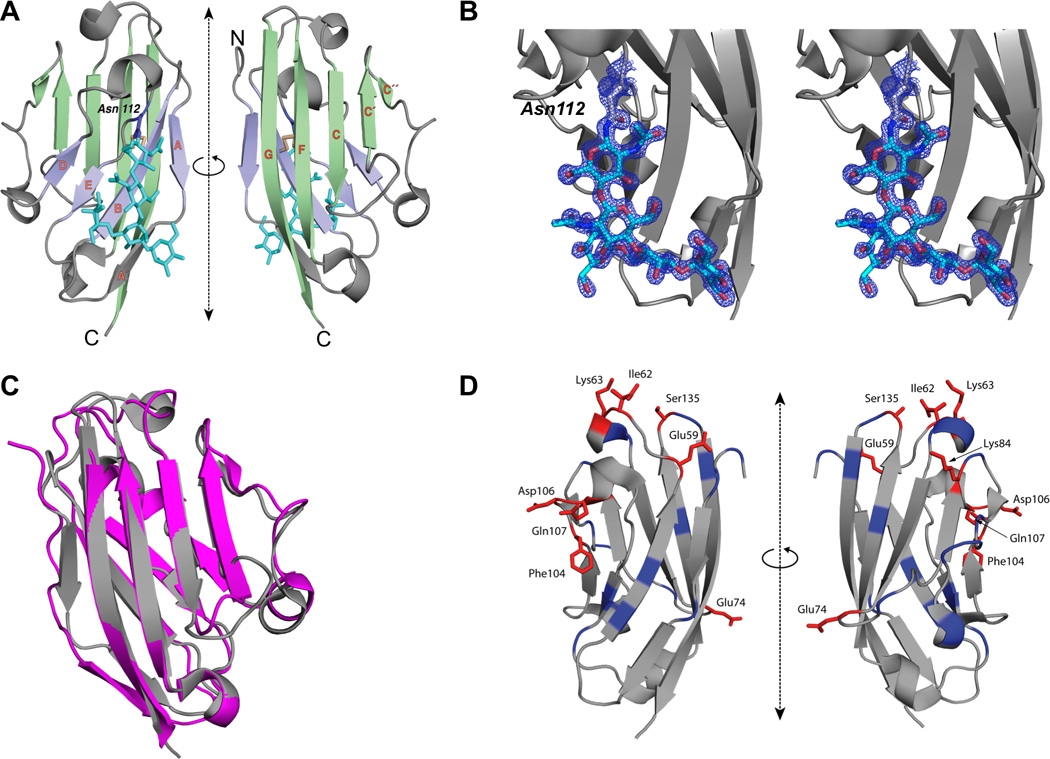
(A) Ribbon representation of the structure of human B7x-IgV (front-sheet: light green, back-sheet: light purple, disulfide: light yellow) is shown in two orientations. The strands of the β-sandwich are labeled in orange; the side chain of Asn112 (purple) and the N-linked glycan (cyan) are shown in stick-figure representation. (B) Electron density observed near Asn112 corresponds to an N-linked glycan. Ribbon representation of the structure of human B7x-IgV (gray) is shown. Electron density map (2Fo–Fc), contoured at +2σ, and covering the area near and including Asn112 is shown in mesh representation (blue). The 5 residues of N-linked glycan are shown in stick representation. (C) Superposition of B7x and PD-L1. Gray represents IgV domain of human PD-L1 and Pink represents IgV domain of human B7x. (D) Ribbon diagram of the IgV domain of B7x showing the location of residues targeted for mutagenesis. Positions that when mutated resulted in at least 40% reduction in 1H3 binding are highlighted in red, while the remainder of targeted positions are highlighted in blue.
