Figure 3.
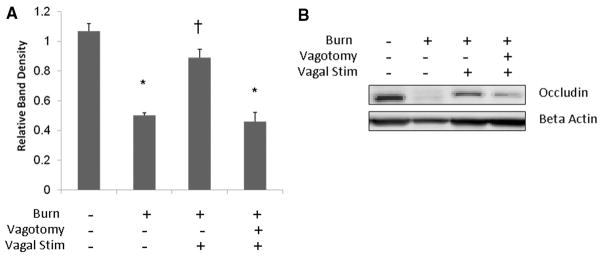
Stimulation of the vagus nerve before injury prevents the burn-induced decrease of intestinal occludin protein expression. Intestinal extracts were obtained from animals 4 hours following injury for measurement of occludin protein expression using Western blot. (A) Graph representing relative band densities from Western blots measuring intestinal occludin protein expression. Vagal nerve stimulation attenuates the loss of occludin protein seen following severe burn. Abdominal vagotomy abrogates the protective effects of vagal nerve stimulation, with occludin expression similar to burn alone. (B) Representative Western blot for intestinal occludin. *p < 0.001 versus Sham, †p < 0.001 versus burn and vagotomy/vagal stimulation/burn.
