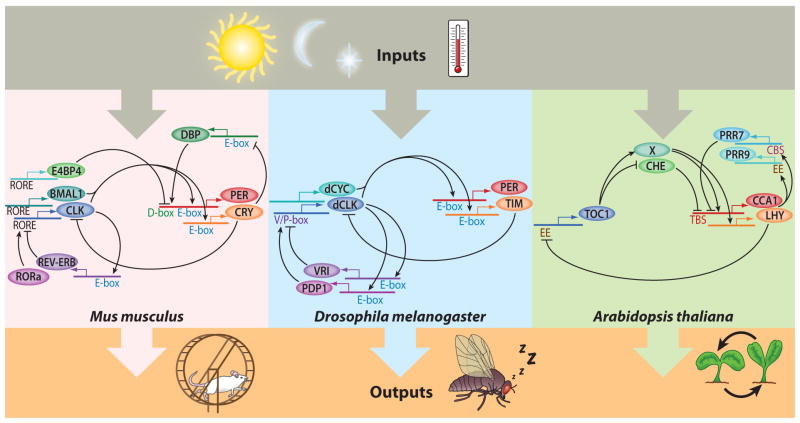
Figure 1.
A simplified schematic model diagram to highlight the similarities between the circadian-clock oscillators of Mus musculus, Drosophila melanogaster, and Arabidopsis thaliana. Abbreviations: BMAL1, brain and muscle ARNT-like 1; CBS, CCA1 binding site; CCA1, CIRCADIAN CLOCK ASSOCIATED 1; CHE, CCA1 hiking expedition; CLK, circadian locomotor output cycles protein kaput; CRY, cryptochrome; DBP, D-box binding protein; dCYC, Drosophila cycle; dCLK, Drosophila circadian locomotor output cycles protein kaput; E4BP4, E4 promoter-binding protein 4; EE, evening element; LHY, late elongated hypocotyl; PDP1, PAR-domain protein 1; PER, period; PRR7, pseudoresponse regulator 7; PRR9, pseudoresponse regulator 9; REV-ERB, reverse erb; RORa, RAR-related orphan receptor A; RORE, REV-ERB/ROR response element; TBS, TCP binding site; TIM, timeless; TOC1, timing of CAB expression 1; V/P-box, Vrille/PDP1 binding box; VRI, Vrille.