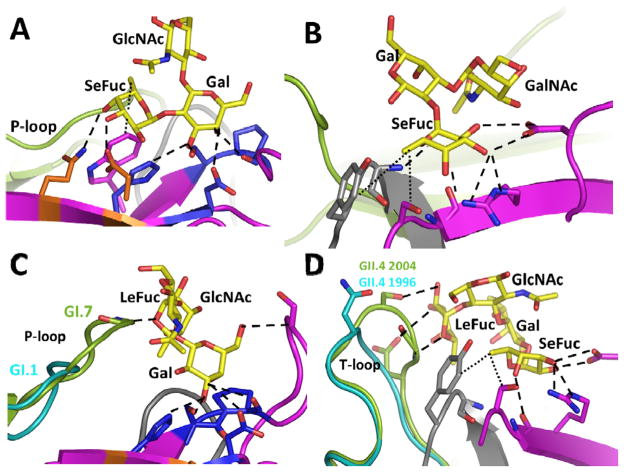
Figure 4.
(A) Gal-centric HBGA interactions in GI NoVs. Shown here as an example is interactions between GI.1 and H-type HBGA. A-type HBGA makes similar interaction with its Gal and N-acetamido groups of N-acetylgalactosamine similar to the Gal and Fuc moieties of the H-type. (B) Fuc-centric HBGA interactions in GII NoVs, shown here as an example is interactions between GII.4 P domain and A-type HBGA (PDB ID: 3SLD). (C) Alterations in length and structure of the P-loop that allows GI.7 bind non-secretor Lea (PDB I.D. 4P3I), GI.1 with a shorter P–loop cannot make similar interactions (D) Structural alterations in the T-loop that allows 2004 GII.4 variant to interact additionally with di-fucosyl secretor Lewis HBGA (Leb) (PDB ID: 3SLD), similar interactions with Leb are not possible in the 1996 GII.4 variant (cyan). The interacting P domain residues are shown as sticks with oxygen and nitrogen atoms in red and blue, respectively.