Figure 1.
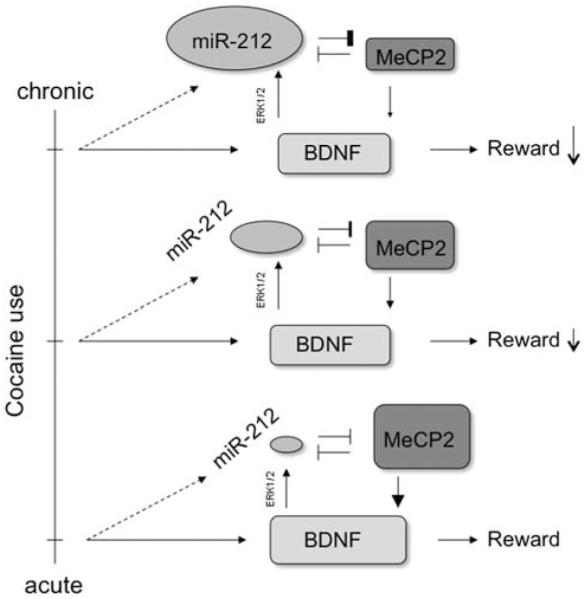
Relation between miR-212, methyl CpG-binding protein (MeCP2), and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) mediates the adaptive response to chronic cocaine exposure. Cocaine increases BDNF concentrations, even after a single dose,78 and BDNF has a strong role in the motivating and rewarding aspects of the drug.86 BDNF signaling at the synapse increases transcription of miR-212 via an extracellular-signal-related kinase (ERK1/2) pathway.37 This miRNA exhibits mutual inhibition with MeCP2, a transcription factor necessary for BDNF expression in response to neural activity.74 The increased expression of miR-212 observed after chronic cocaine treatment72 therefore represents a mechanism of tolerance by inhibiting activity-dependent BDNF transcription in the nucleus accumbens.
