Figure 5. IFN induction by HCV in the liver.
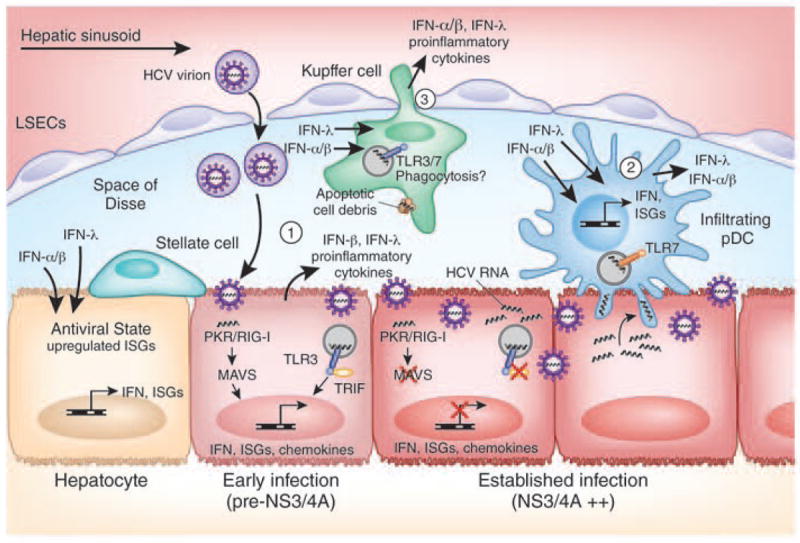
The liver contains different cell types that can secrete IFN upon stimulation by HCV infection, including (1) hepatocytes, (2) infiltrating plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs), and (3) Kupffer cells. The activation of these cells is required to prime the adaptive immune response to HCV, which plays a major role in eventual viral clearance16. Both type I and type III IFN can act on uninfected hepatocytes to induce an antiviral state that limits virus spread. In the infected cell, HCV can evade IFN induction through viral-mediated processes, including NS3/4A-mediated cleavage of MAVS and TRIF, impacting HCV outcome of infection and disease progression. Cross-talk between hepatocytes and hepatic stellate cells during HCV infection has also been shown to induce inflammatory cytokines and chemokines (not depicted here)100.
