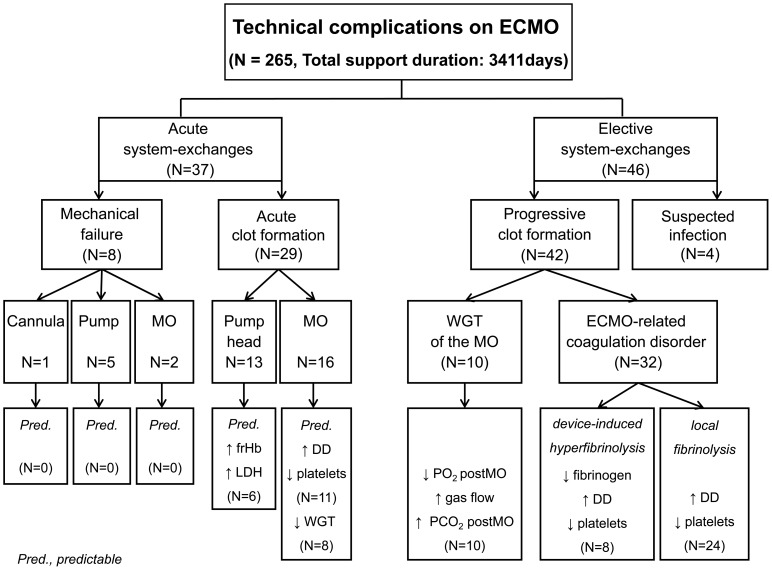
Figure 1. Retrospective analysis of reasons for acute and elective system-exchange during vvECMO.
Acute exchanges were all events that required an immediate intervention of perfusionists. Mechanical failure was defined as leakage at the MO, pump head problems, dysfunction of the pumpdrive, cannula or circuit rupture. Acute clot formation within the MO caused a severe increase in the pressure drop across the MO (dpMO) followed by a decrease in blood flow, while acute clot formation in the pump head was indicated by a dramatic increase in plasma free hemoglobin concentration. Suspected infection based on clinical observations (see text). Progressive clot formation was observed in almost all remaining MOs, which caused a worsened gas exchange capability of the MO (decrease in pO2 postMO, increase in pCO2 postMO, increase in sweep gas flow) and an alteration in coagulation parameters (increase in D-dimer levels, decrease in fibrinogen levels and decrease in platelet counts).