Figure 1.
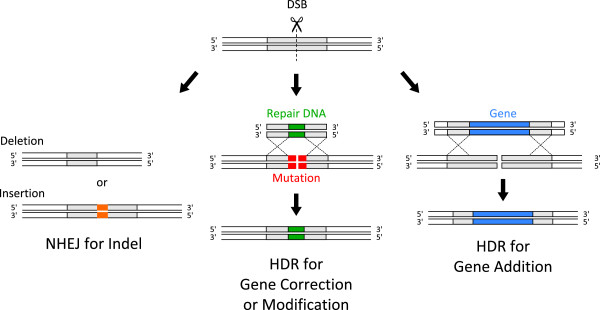
Engineered nuclease-induced genome editing pathways. Double-stranded breaks (DSBs) are induced at a targeted sequence by a microorganism-originated, engineered nuclease. Non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) is a DSB repair pathway that ligates or joins two broken ends together, resulting in the introduction of small insertions or deletions (indels) at the site of the DSB. Homology-directed repair (HDR) is a DNA template-dependent pathway for DSB repair, using a homology-containing donor template along with a site-specific nuclease, enabling the insertion of single or multiple transgenes (gene addition) in addition to single-nucleotide substitutions in which an amino acid substitution of a protein occurs (gene modification), or a mutation is completely repaired in the resultant organism genome (gene correction).
