Figure 2.
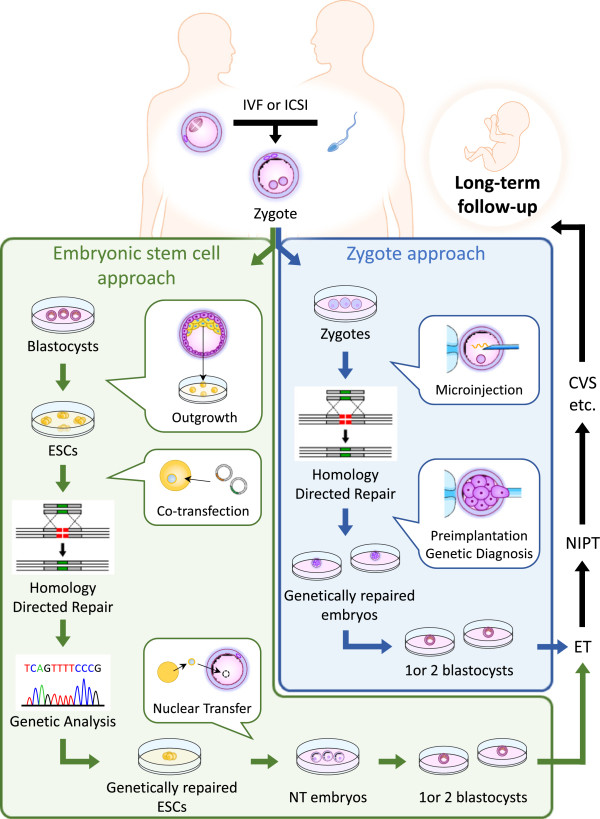
Embryonic stem cell approach and zygote approach for genome editing-mediated gene correction to prevent a genetic disease. Zygotes with a mutation are treated with genome editing-mediated gene correction via embryonic stem cell approach or zygote approach. After embryo screening by preimplantation genetic diagnosis, one or more embryos which have a corrected gene with no off-target mutations are subjected to embryo transfer. NIPT can be used to confirm the genetic condition of the fetus. Subsequently, CVS or amniocentesis can confirm whether a fetus has genetic mosaic mutations. Long-term follow-up is required even after a successful birth owing to the contribution of the modified germline to the entire body. CVS: chorionic villus sampling, ESCs: embryonic stem cells, ET: embryo transfer, ICSI: intracytoplasmic sperm injection, IVF: in vitro fertilization, NIPT: non-invasive prenatal genetic testing, NT: nuclear transfer.
