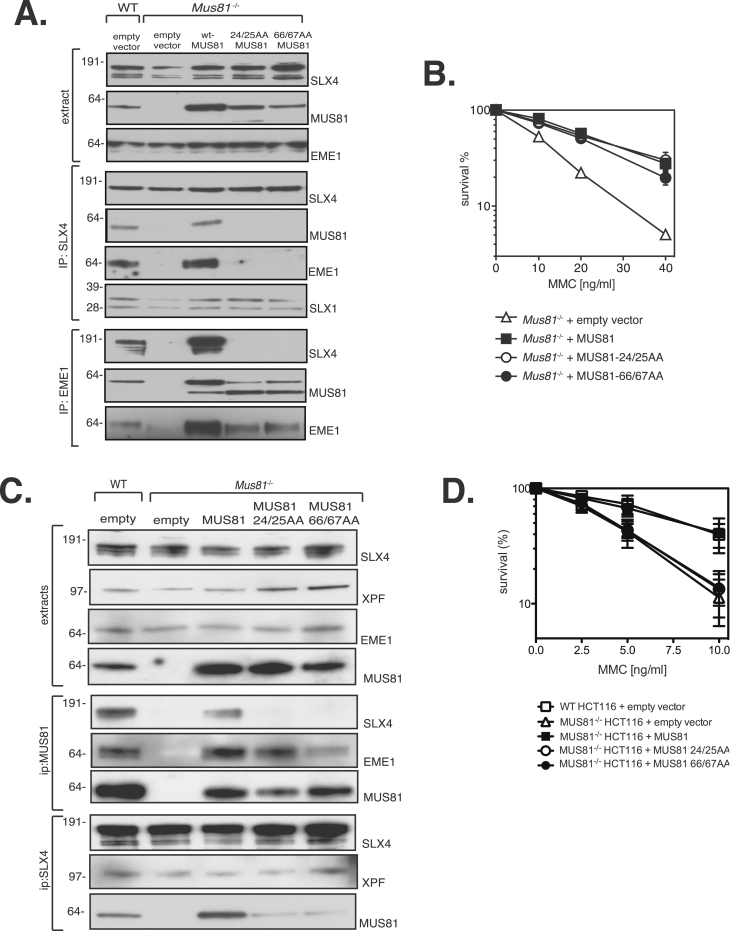
Fig. 2.
MUS81 mutations that cannot interact with SLX4 cause ICL repair defects in human cells but not mouse cells. (A) Mus81−/− MEFs were infected with retroviruses expressing wild-type MUS81, MUS81 24/25AA or MUS81 66/67AA. Wild-type MEFs (WT) and Mus81−/− MEFs infected with empty virus were used as controls. Extracts were subjected to western blotting to test expression (upper panel) or immunoprecipitation with anti-SLX4 (middle panel) and anti-EME1 antibodies (lower panel). (B) Clonogenic survival analysis of Mus81−/− MEFs stably expressing MUS81, MUS81 24/25AA or MUS81 66/67AA, exposed to MMC. For each genotype, cell viability of untreated cells was defined as 100%. Mus81−/− MEFs infected with empty virus were used as controls. Data are represented as mean ± SEM, n = 3. (C) MUS81−/− HCT116 cells were infected with retroviruses expressing MUS81, MUS81 24/25AA or MUS81 66/67AA. Wild-type cells (WT) and MUS81−/− HCT116 cells infected with empty virus were used as controls. Extracts were subjected to western blotting to test expression (upper panel) or immunoprecipitation with anti-MUS81 and anti-SLX4 antibodies (lower panel). (D) Clonogenic survival analysis of MUS81−/− HCT116 cells stably expressing MUS81, MUS81 24/25AA or MUS81 66/67AA, exposed to MMC. For each genotype, cell viability of untreated cells was defined as 100%. Wild-type HCT116 and MUS81−/− HCT116 cells infected with empty virus were used as controls. Data are represented as mean ± SEM, n = 3.