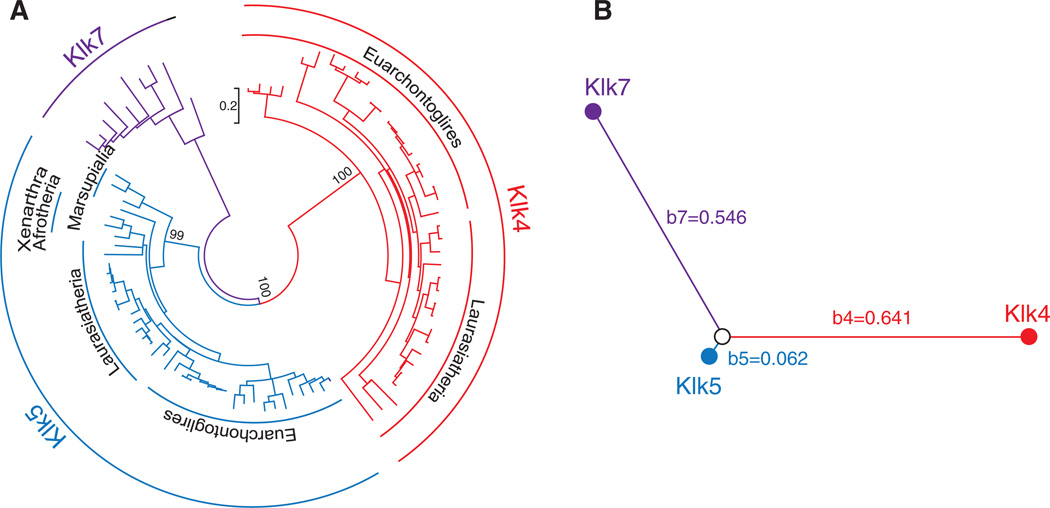
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic tree of the Klk4, Klk5 and Klk7 genes (A) and the type-I functional branch lengths of these genes (B). (A) This tree was constructed by the ML method based on the JTT+G+I amino acid substitution model. The branches to Klk4 (Euarchontoglires and Laurasiatheria), Klk5 (Euarchontoglires, Laurasiatheria, Xenarthra/Afrotheria and Marsupialia) and Klk7 are supported by a bootstrap value of 99–100%. The scale is shown between Klk4 and Klk7. (B) The type-I branch lengths of each KLK gene cluster from their common ancestral gene, calculated using Diverge 2.0 (b4 = 0.641, b5 = 0.062, and b7 = 0.546), are illustrated. Note that b5 is much shorter than b4 (and b7), suggesting a functional divergence of Klk4 from Klk5.