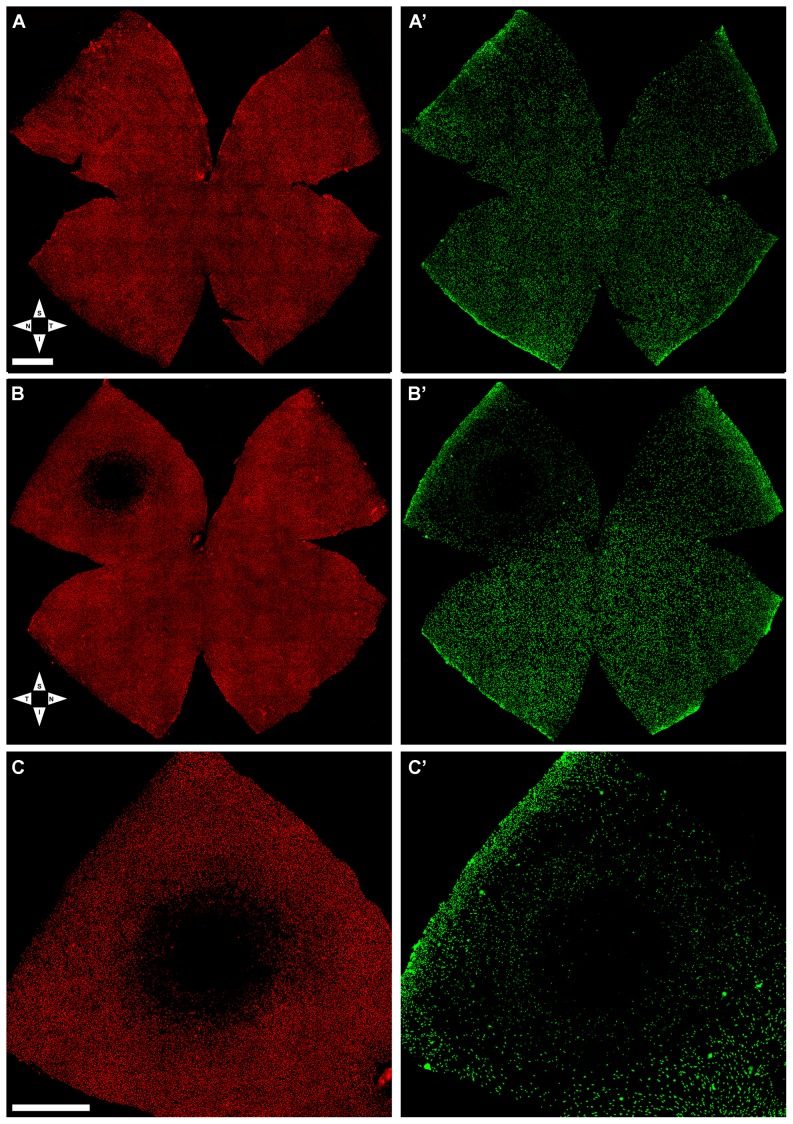
Figure 5. Light-induced focal damage to the cone-photoreceptor population.
Wholemount of the fellow-right (unexposed) (A,A′) and the left (light exposed) (B,B′) retinas from a representative rat seven days after blue-light emitting diode induced retinal phototoxicity. L- (A,B,C) and S- (A′,B′,C′) cones were labelled with antibodies against the different opsins. A,A′. In the control retina, L- (A) and S-cones (A′) appear normally distributed throughout the retina. B,B′. The light exposed retina (same retina illustrated in Figs.3–4), shows a small region with reduced densities of L- and S-cones in the superotemporal quadrant at approximately 3.4 mm from the optic disc. Note that the area is larger for the S- than for the L-opsin. C, C′. Details of the superotemporal quadrant of the same retina (shown in B,B′) demonstrating the typical circular damage induced by phototoxicity. S, superior; T, temporal; I, inferior; N, nasal. Bar: 1 mm.