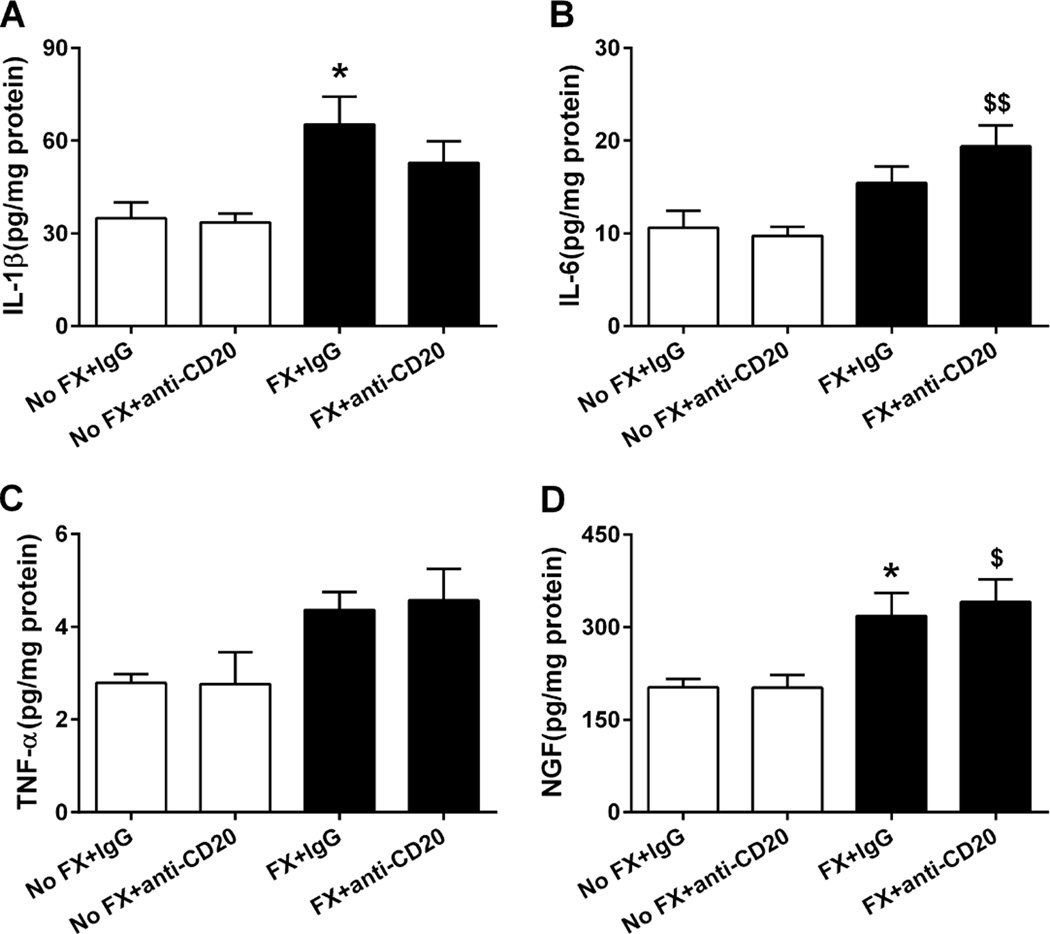
Fig. 9.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay analysis for skin inflammatory cytokines and nerve growth factor (NGF) levels in fracture (FX) and control mice treated with either anti-CD20 or control immunoglobulin G (IgG; n = 8 per cohort). Anti-CD20 alone did not change cytokine levels in the controls. At 3 weeks post fracture, hind paw skin interleukin (IL)-1β (A), IL-6 (B), tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α (C), and NGF (D) protein levels all were increased in fracture mice treated with control IgG, and anti-CD20 treatment had no effect on fracture induced upregulation of the cutaneous inflammatory mediators. Data were analyzed using a 2-way analysis of variance with Bonferroni correction for post hoc contrasts. *P < 0.05 for FX+IgG (n = 8) vs No FX+IgG (n = 8), $P < 0.05, $$P < 0.01, for FX+anti-CD20 (n = 8) vs No FX+anti-CD20 (n = 8). Data are expressed as mean values ± SEM.