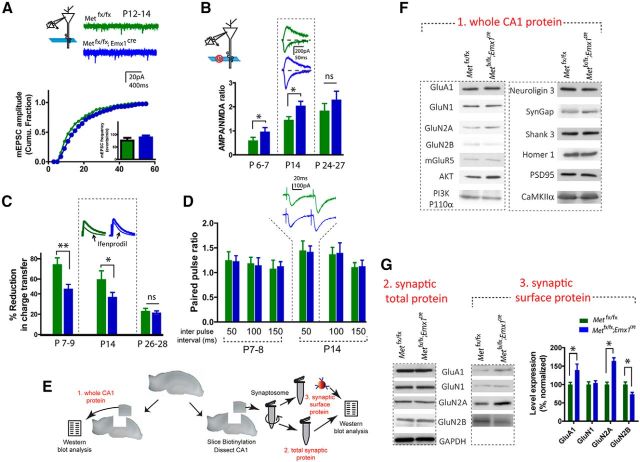
Figure 5.
MET loss of function leads to accelerated glutamatergic circuit maturation. A, Analysis of mEPSC in P12–P14 acute hippocampal slices revealed an enlarged mEPSC amplitude in Metfx/fx; emx1cre neurons (p < 0.02). B, Metfx/fx; emx1cre CA1 neurons in P6–P7 and P14 slices show significantly increased A:N ratio (*p < 0.05). C, Metfx/fx; emx1cre CA1 neurons in P7–P9 and P14 slices show significantly decreased sensitivity to ifenprodil (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01), as measured by reduction of NMDAR current after ifenprodil (3 μm). D, No change of paired pulse ratio was found at various interpulse intervals at both P7–P8 and P14. E, Illustration of isolation of whole CA1 tissue lysate (1), total synaptosome protein (2), and synaptic surface protein (3), and quantification protocol. F, Representative Western blot of different glutamate receptor subunit proteins, postsynaptic scaffold proteins, and signaling molecules in whole CA1 lysates. G, Representative blots and quantification of glutamate receptor subunits in total synaptosome fraction and synaptic membrane surface compartments. Quantitative analysis of synaptic surface proteins revealed increased GluA1, GluN2A, and decreased GluN2B levels of immunoreactive protein (*p < 0.05). No significant change of total synaptosome protein was seen (quantification not shown).