Figure 4.
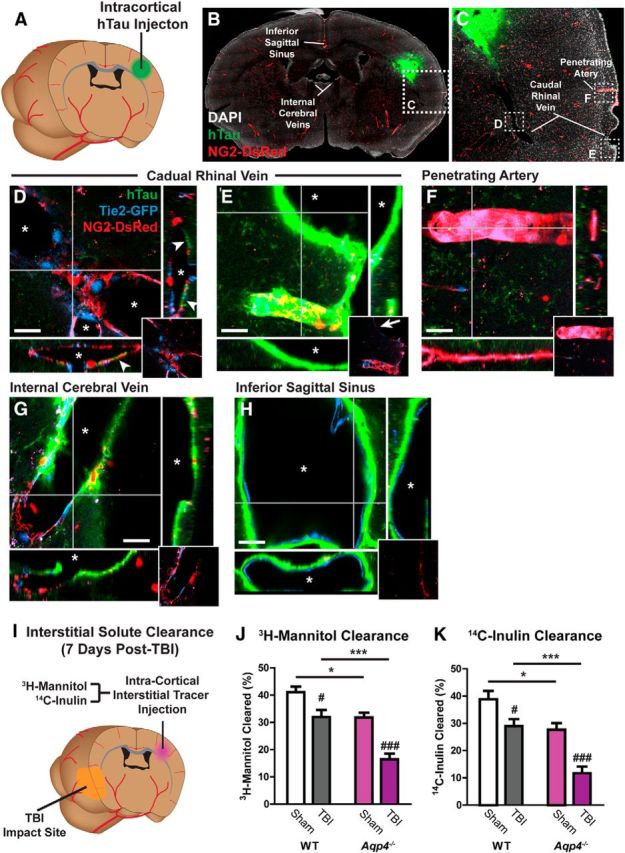
Interstitial tau is cleared along the paravascular glymphatic pathway. A, Recombinant hTau was injected into the cortex of Tie2-GFP:NG2-DsRed double-transgenic mice, which express GFP in the vascular endothelium and DsRed fluorescent protein in cerebral vascular smooth muscle and pericytes. B–H, Movement of interstitial hTau through the intact brain was evaluated 30 min post injection by immunofluorescence. hTau moved diffusely from the injection site (B, C), moving along subcortical white matter tracks and perivascular spaces, to exit the brain along large draining veins. High-power micrographs of the intraparenchymal segment (D) and the exit site from the brain (E) of the caudal rhinal vein show hTau accumulation (arrowheads) in paravascular spaces surrounding this vein. This includes the wall of the large surface venous structure present at the brain surface (arrow). Insets depict X-Z and Y-Z orthogonal views of confocal stack. Inset at bottom right depicts vascular reporter proteins without hTau fluorescence channel. Asterisk denotes vessel lumen. F, The absence of hTau along a nearby penetrating artery shows that para-arterial spaces are not long-range pathways for interstitial hTau clearance. Intense hTau labeling of the distant medial internal cerebral veins (G) and the inferior sagittal sinus (H) shows that these venous structures are major outflow routes for interstitial hTau. Scale bars: 20 μm. I, The effect of TBI upon interstitial solute clearance from the cortex was evaluated 7 d post injury. The clearance of radiolabeled 3H-mannitol (MW 182 Da; J) and 14C-inulin (MW∼5 kDa; K) was measured 60 min after infusion into contralateral frontal cortex. In wild-type mice, TBI significantly slowed the clearance of both 3H-mannitol and 14C-inulin (#p < 0.05, ###p < 0.001 TBI vs sham; two-way ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test for multiple comparisons; n = 6 animals per group). Clearance studies conducted in Aqp4−/− mice demonstrated that impairment of solute clearance after TBI was exacerbated by Aqp4 gene deletion (*p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001 wild-type vs Aqp4−/− mice; two-way ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test for multiple comparisons, n = 6 animals per group).
