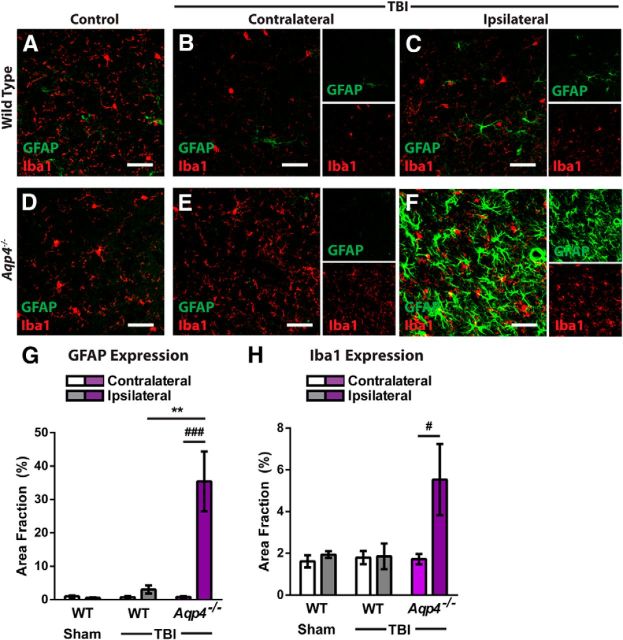
Figure 8.
Aqp4 gene deletion promotes neuroinflammation after TBI. The effect of Aqp4 gene deletion upon the persistence of neuroinflammation after TBI was evaluated. A–F, Wild-type and Aqp4−/− mice were subjected to TBI and reactive astrogliosis (GFAP expression), and microgliosis (Iba1 expression) in the contralateral and ipsilateral cortex was evaluated by immunofluorescence 28 d post injury. Compared with wild-type mice after TBI, markedly elevated GFAP- and Iba1-immunoreactivity were observed in the ipsilateral cortex of Aqp4−/− mice after TBI. G, Quantification of GFAP labeling demonstrated significantly increased reactive astrogliosis in the ipsilateral cortex of Aqp4−/− mice (###p < 0.001, Ipsilateral vs Contralateral Aqp4−/−; two-way ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test for multiple comparisons; n = 4 animals per group), which was not present in wild-type mice (**p < 0.01, Aqp4−/− Ipsilateral vs WT Ipsilateral). H, Quantification of Iba1 labeling showed that microglial activation was similarly increased in the ipsilateral cortex of Aqp4−/− mice (#p < 0.05, Ipsilateral vs Contralateral Aqp4−/−).