Figure 10.
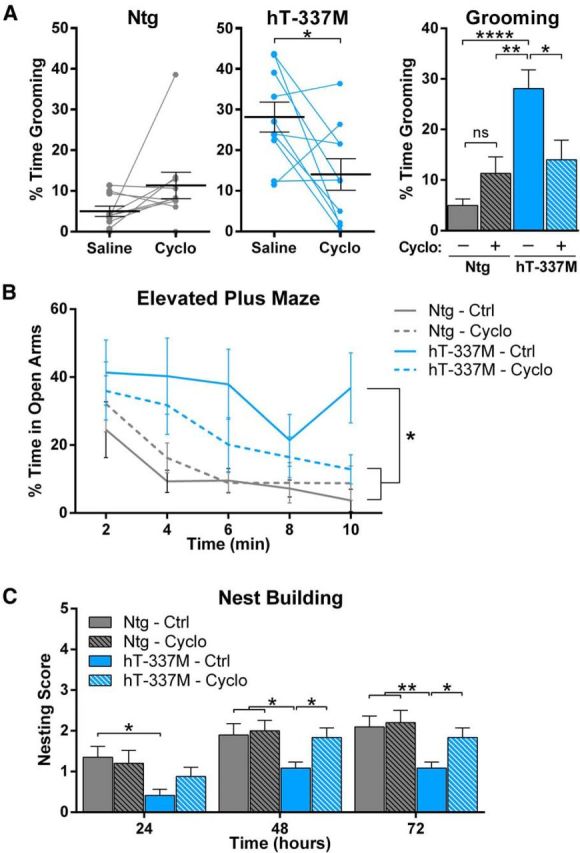
Increasing NMDAR function alleviates behavioral abnormalities in hT-337M mice. A, Percentage of time grooming in Ntg (left) and hT-337M (middle) mice after treatment with either saline or cycloserine (Cyclo). Cycloserine significantly decreased grooming in hT-337M mice (each line is one mouse). *p < 0.05 by paired t test. Right, Grouped data. n = 10 mice per genotype receiving each treatment. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001 with two-way ANOVA and Tukey's multiple comparisons test. B, C, Two week treatment with either control or cycloserine diet in 18-month-old animals. n = 10 Ntg mice for each treatment, n = 12 hT-337M for each treatment. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 with two-way ANOVA and Newman–Keuls multiple comparisons test. B, hT-337M treated with cycloserine spent significantly less time in the open arms of EPM than untreated hT-337M mice. C, hT-337M treated with cycloserine built significantly better nests than untreated hT-337M mice.
