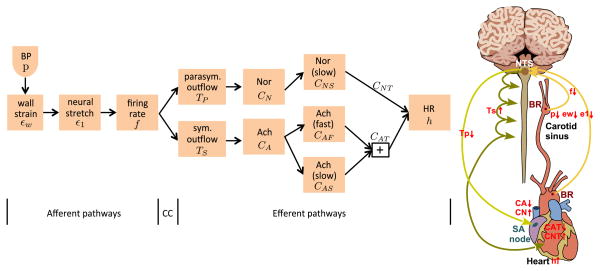
Figure 1.
Model components and physiological pathways. Left panel: CC denotes the control center (located within the nucleus solitary tract), which integrates all sensory inputs. Right panel: A drop in blood pressure (p) detected at aortic and carotid sinus baroreceptors causes a decrease in stretch of the vessel wall (εW) and subsequently the baroreceptor neurons (ε1), as a result afferent firing rate (f) decreases inhibiting/stimulating parasympathetic (TP) and sympathetic (TS) outflow, inhibiting/stimulating the release of acetylcholine (CA)/noradrenaline (CN). Total intercellular compounds associated with acetylcholine (CAT) and noradrenaline (CNT) are inhibited and stimulated, respectively leading to an increase in heart rate (h).