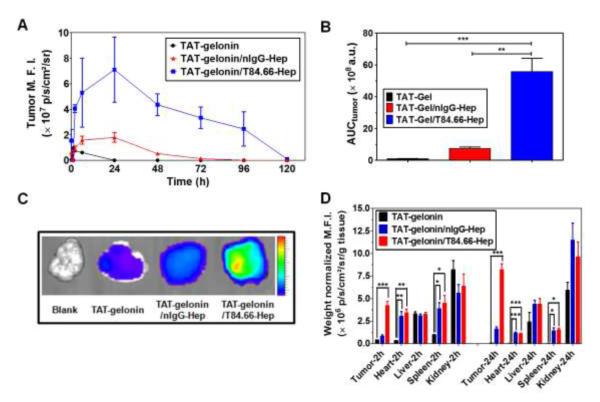
Figure 10.
Tumor accumulation profiles of TAT-gelonin-B4 after administration of LS174T s.c. xenograft tumor bearing nude mice with TAT-gelonin-B4, TAT-gelonin-B4/nIgG-Hep or TAT-gelonin-B4/T84.66-Hep-C5. (A) Relative mean fluorescence intensities (M.F.I.s) corresponding to TAT-gelonin-B4 in the tumors as a function of time. (B) Comparison of area under the curves (AUCtumor) of the tumor M.F.I. vs. time curves, corresponding to the tumor exposures of TAT-gelonin-B4. The tumor exposure of TAT-gelonin-B4 was significantly enhanced (58.4-fold) by administration of TAT-gelonin-B4/T84.66-Hep-C5, when compared with administration of TAT-gelonin-B4 alone. Statistical significant difference of the AUCtumor among the groups was compared by 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test as the post hoc test using Prism software (GraphPad). **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. (C) Tumor images dissected 6 h after administration of the test compounds. (D) Biodistribution profiles at 2 h and 24 h post-administration. In agreement of the observations in Fig. 8A and 8B, remarkably enhanced accumulation of TAT-gelonin-B4 was observed in the tumor dissected from the mouse administered with TAT-gelonin-B4/T84.66-Hep-C5, compared with injection of TAT-gelonin-B4 alone. 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test as the post hoc test using Prism software (GraphPad). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. (TAT-gelonin-B4: Dylight 775-B4 labeled chimeric TAT-gelonin fusion protein, nIgG-Hep: nonspecific IgG-heparin conjugate, T84.66-Hep-C5: Dylight 679-C5 labeled T84.66-heparin conjugate)